Bauxite is the primary ore used in aluminum production. The ore consists largely of aluminum oxide compounds and is typically found in tropical and subtropical regions. The top producers of bauxite include Australia, China, Brazil, and India. These countries possess the necessary conditions for bauxite deposits, such as the right climate and geological features.
Composition and Formation of Bauxite
Bauxite is formed through the weathering of aluminum-rich rocks in a process that takes millions of years. This process involves the leaching of silica and other soluble elements, leaving behind a concentration of aluminum oxides. The composition of bauxite can vary significantly depending on its geographical locati0n and the conditions under which it formed.
Geographical Distribution
Bauxite deposits are predominantly found in regions with a tropical climate where intense weathering processes have occurred. Australia leads the world in bauxite production, followed by China, Guinea, and Brazil. These regions not only have abundant bauxite reserves but also have the infrastructure and technology necessary for efficient mining operations.
Economic Importance
The economic impact of bauxite mining is profound, especially for countries with large deposits. It contributes significantly to their GDP and creates numerous job opportunities. The export of bauxite and its by-products is a major source of foreign exchange, which supports the economic stability of these nations.
Where is Aluminum Mined?
Global Distribution of Bauxite Mines
Aluminum mining is concentrated in specific regions around the world. Australia holds the largest bauxite reserves, accounting for about one-third of global production. The country’s vast reserves and high-quality ore make it a key player in the aluminum industry.
Key Mining Regions
- Australia: Known for its rich deposits, Australia is home to several major bauxite mines. The Weipa mine in Queensland is one of the largest, producing millions of tons of bauxite annually. The country’s commitment to mining sustainability is reflected in its advanced technologies and environmental management practices.
- China: As both a leading producer and consumer of bauxite, China’s mining operations are crucial to its industrial needs. The country imports additional bauxite to meet its demand, reflecting its significant role in the global aluminum market. China’s focus on technological advancement in mining has helped improve efficiency and reduce environmental impact.
- Brazil and India: Both countries have large deposits and are significant exporters of bauxite, contributing to the global supply chain. Brazil’s rich deposits have made it a powerhouse in the mining industry, while India’s recent investments in mining technology are poised to increase its output.
Strategic Importance
The strategic importance of bauxite mining cannot be overstated. As the demand for aluminum increases globally, countries with significant bauxite reserves have a substantial advantage. The ability to control a crucial component of the supply chain gives these nations significant economic and geopolitical leverage.
What Do I Need to Mine Aluminum Ore?

Mining aluminum ore requires several essential components, including technology, labor, and environmental management strategies. Here’s a closer look at these elements:
Equipment and Technology
Mining bauxite involves several stages: clearing the land, extracting the ore, and processing it into alumina. This requires heavy machinery such as bulldozers, excavators, and haul trucks to transport the ore. Advanced technology is also used to ensure efficient and sustainable extraction processes.
Advanced Mining Technologies
The introduction of advanced technologies such as remote sensing, automation, and data analytics has revolutionized bauxite mining. These technologies allow for more precise extraction, reducing waste and improving safety. Automation in particular has decreased the need for human labor in hazardous areas, thus enhancing worker safety.
Processing and Refining
Once bauxite is extracted, it must be processed into alumina before it can be used to produce aluminum. This involves crushing and grinding the ore, followed by chemical treatment to remove impurities. The Bayer process is the most common method used to refine bauxite into alumina, which is then smelted to produce aluminum.
Innovations in Equipment
Modern mining equipment is designed to be more efficient and environmentally friendly. Innovations in machinery have reduced emissions and energy consumption, contributing to more sustainable mining practices. Equipment manufacturers are continually developing new technologies to further enhance efficiency and reduce the environmental footprint of mining operations.
Workforce
A skilled workforce is vital for successful mining operations. Miners, engineers, and environmental specialists work together to ensure that bauxite is extracted safely and efficiently, minimizing the impact on the environment and surrounding communities.
Training and Development
Continuous training and development are essential for maintaining a skilled workforce in the mining industry. Workers must be trained in the latest technologies and safety protocols to ensure efficient and safe operations. Investment in workforce development is crucial for keeping pace with technological advancements and regulatory changes.
Safety Measures
Ensuring the safety of workers is a top priority in the mining industry. This includes implementing strict safety protocols, regular training, and investing in safety equipment. The use of personal protective equipment and advanced monitoring systems helps prevent accidents and protect workers’ health.
Community Engagement
Mining operations often have a significant impact on local communities. Engaging with these communities is crucial for gaining social license to operate and ensuring that the benefits of mining are shared. This includes providing employment opportunities, supporting local infrastructure, and involving community members in decision-making processes.
Environmental Management
Implementing environmental management practices is crucial in reducing the negative impacts of aluminum mining. This includes rehabilitation plans to restore mined land, strategies to manage waste and tailings, and measures to protect local ecosystems and biodiversity.
Rehabilitation and Restoration
Post-mining rehabilitation is essential in restoring ecosystems. Replanting native vegetation, rebuilding habitats, and monitoring biodiversity are crucial steps in this process. Successful rehabilitation requires collaboration between mining companies, governments, and environmental organizations to ensure that land is returned to a sustainable state.
Waste Management
Effective waste management is critical in minimizing the environmental impact of mining. This involves managing tailings, reducing waste generation, and recycling materials where possible. Innovative waste management strategies can help reduce the environmental footprint of mining operations and contribute to more sustainable practices.
Biodiversity Conservation
Protecting local ecosystems and biodiversity is a key aspect of environmental management in mining. This includes conducting environmental impact assessments, implementing conservation plans, and monitoring the impacts of mining activities on local flora and fauna. Efforts to preserve biodiversity help maintain ecological balance and support the long-term sustainability of mining regions.
The Role of Aluminum Miners
Aluminum miners play a critical role in the extraction process. They are responsible for operating machinery, monitoring extraction processes, and ensuring that safety protocols are followed. Their work is essential in maintaining production efficiency and minimizing environmental disruption.
Operational Responsibilities
Miners are tasked with various operational responsibilities, including the operation of heavy machinery, monitoring of extraction processes, and adherence to safety standards. Their expertise ensures that mining operations run smoothly, efficiently, and safely.
Monitoring and Safety Protocols
Ensuring safety and compliance with environmental regulations is a key responsibility of miners. This involves regular monitoring of mining activities, adherence to safety protocols, and reporting any issues or incidents. Miners play a crucial role in maintaining a safe working environment and minimizing the environmental impact of mining operations.
Skill Development and Training
Continuous skill development and training are essential for miners to stay updated with the latest technologies and safety protocols. Ongoing training programs help miners enhance their skills, improve efficiency, and ensure compliance with industry standards.
The Environmental Impact of Aluminum Mining
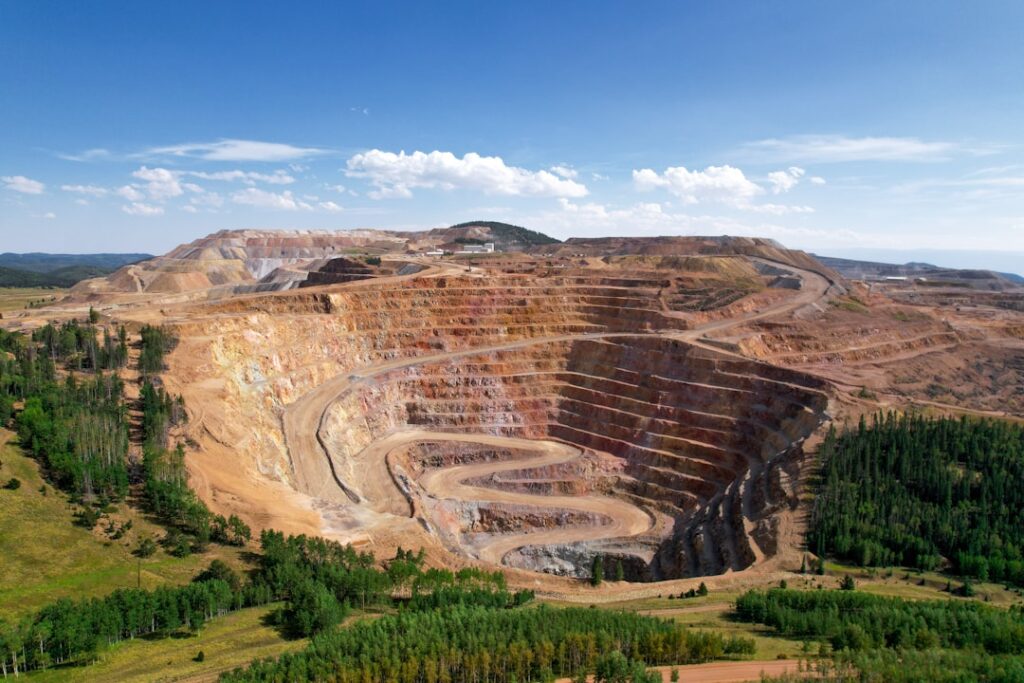

by Noah Ridge (https://unsplash.com/@consoledotlog)
While aluminum is a valuable resource, mining it comes with several environmental challenges. Understanding these impacts is crucial for developing more sustainable mining practices.
Land Degradation and Habitat Loss
The process of clearing land for bauxite mining can lead to significant deforestation and habitat destruction. This not only affects plant and animal species but also disrupts the ecological balance of the area. Rehabilitation efforts are necessary to restore these lands post-mining.
Deforestation
Deforestation is a major concern in bauxite mining areas. The removal of vegetation for mining operations leads to habitat loss for many species and disrupts local ecosystems. Efforts to combat deforestation include reforestation projects and the implementation of land-use planning strategies to minimize the impact on forests.
Habitat Fragmentation
Mining operations often lead to habitat fragmentation, which can isolate species and reduce biodiversity. This fragmentation disrupts migration patterns and breeding grounds, threatening the survival of many species. Conservation strategies focus on creating wildlife corridors and protected areas to mitigate these effects.
Ecological Imbalance
The disruption of ecosystems due to mining activities can lead to ecological imbalances, affecting the health of local environments. This includes changes in soil composition, water availability, and the introduction of invasive species. Restoring ecological balance requires comprehensive environmental management plans and collaboration between stakeholders.
Water Pollution
Mining operations can lead to water pollution through the release of harmful chemicals and sediments into nearby water bodies. This can have detrimental effects on aquatic life and the quality of water available for local communities.
Chemical Contamination
The use of chemicals in the extraction and processing of bauxite can result in contamination of local water sources. This poses a risk to aquatic ecosystems and human health. Implementing effective waste management and water treatment systems is crucial in preventing chemical contamination.
Sedimentation
Mining activities can increase sedimentation in nearby water bodies, affecting water quality and aquatic habitats. Sedimentation can smother aquatic plants and animals, reducing biodiversity and disrupting ecosystems. Strategies to reduce sedimentation include erosion control measures and sediment management plans.
Impact on Local Communities
Water pollution from mining operations can affect the availability and quality of water for local communities. This can have serious implications for health, agriculture, and livelihoods. Engaging with communities and implementing measures to protect water resources are essential in addressing these impacts.
Air Pollution
The extraction and processing of bauxite release dust and greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. This contributes to air pollution and climate change, making it essential for mining companies to adopt cleaner technologies and emissions-reduction strategies.
Dust Emissions
Mining activities generate large amounts of dust, which can affect air quality and pose health risks to workers and nearby communities. Dust suppression techniques, such as water spraying and vegetation barriers, are important in reducing dust emissions.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
The energy-intensive nature of bauxite mining and refining contributes to greenhouse gas emissions. These emissions contribute to climate change and necessitate the adoption of cleaner technologies and renewable energy sources to reduce the carbon footprint of mining operations.
Health Impacts
Air pollution from mining operations can have serious health impacts on workers and local communities, including respiratory issues and other illnesses. Implementing health and safety measures, such as air quality monitoring and protective equipment, is crucial in protecting the health of those affected.
Energy Consumption
The mining and refining of aluminum are energy-intensive processes. Reducing energy consumption through the use of renewable resources and more efficient technologies is vital in minimizing the environmental footprint of aluminum production.
Renewable Energy Integration
Integrating renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, into mining operations can significantly reduce energy consumption and emissions. This transition to renewable energy not only supports sustainability goals but also reduces operational costs in the long run.
Energy Efficiency Technologies
The adoption of energy-efficient technologies and practices in mining operations can lead to significant energy savings. This includes optimizing equipment, improving process efficiency, and implementing energy management systems to monitor and reduce energy use.
Life Cycle Assessment
Conducting life cycle assessments of mining operations helps identify opportunities for reducing energy consumption and environmental impact. This holistic approach evaluates the entire life cycle of aluminum production, from extraction to end-use, and informs strategies for sustainable practices.
Towards Sustainable Aluminum Mining
To address the environmental challenges of aluminum mining, several strategies can be implemented:
Improved Mining Practices
Adopting more sustainable mining practices can significantly reduce environmental impacts. This includes efficient land-use planning, minimizing waste generation, and implementing advanced technologies for cleaner production.
Land-Use Planning
Strategic land-use planning helps optimize the use of land for mining while minimizing environmental impacts. This includes assessing the suitability of areas for mining, avoiding ecologically sensitive regions, and planning for post-mining land use.
Waste Reduction Strategies
Implementing waste reduction strategies, such as recycling and reusing materials, can significantly decrease the environmental footprint of mining operations. Encouraging the circular economy approach in the mining industry promotes sustainability and resource efficiency.
Cleaner Production Technologies
Investing in cleaner production technologies reduces emissions and waste, contributing to more sustainable mining practices. These technologies not only improve environmental performance but also enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs.
Rehabilitation and Restoration
Post-mining rehabilitation is essential in restoring ecosystems. Replanting native vegetation, rebuilding habitats, and monitoring biodiversity are crucial steps in this process.
Reforestation Initiatives
Reforestation initiatives aim to restore vegetation cover in mined areas, providing habitats for wildlife and improving soil stability. These projects often involve collaboration with local communities and environmental organizations to ensure success.
Habitat Restoration
Restoring habitats involves re-establishing the natural conditions of mined areas, including soil composition, vegetation, and water systems. This process requires careful planning and monitoring to ensure long-term ecological recovery.
Biodiversity Monitoring
Monitoring biodiversity in rehabilitated areas helps track the success of restoration efforts and informs future conservation strategies. This involves regular assessments of flora and fauna populations, as well as the overall health of ecosystems.
Community Engagement
Engaging with local communities is important in ensuring that their needs and concerns are addressed. This includes providing employment opportunities, supporting local infrastructure, and involving community members in decision-making processes.
Employment and Economic Benefits
Mining operations can provide significant economic benefits to local communities through job creation and infrastructure development. Ensuring that these benefits are equitably distributed is crucial for gaining community support and fostering sustainable development.
Infrastructure Development
Investing in local infrastructure, such as roads, schools, and healthcare facilities, can improve the quality of life for communities affected by mining operations. These investments support long-term economic growth and contribute to social well-being.
Participatory Decision-Making
Involving community members in decision-making processes helps ensure that mining operations align with local needs and priorities. This participatory approach fosters transparency, trust, and collaboration between mining companies and communities.
Regulatory Frameworks
Strong regulatory frameworks can enforce environmental standards and ensure that mining companies operate responsibly. This includes setting limits on emissions, waste management, and land use.
Environmental Regulations
Robust environmental regulations are essential for guiding sustainable mining practices. These regulations set standards for emissions, waste management, and land rehabilitation, ensuring that mining operations minimize their environmental impact.
Compliance and Monitoring
Regular compliance checks and monitoring are necessary to ensure that mining companies adhere to environmental regulations. This involves inspections, reporting, and enforcement actions to address non-compliance and promote responsible practices.
Policy Development
Developing and updating policies related to mining and environmental protection is crucial for addressing emerging challenges and opportunities. This includes fostering innovation, supporting sustainable practices, and aligning with international environmental standards.
Conclusion
Aluminum mining is essential for meeting global demand for this versatile metal. However, the environmental impacts of mining are significant and must be addressed through sustainable practices. By adopting advanced technologies, engaging with communities, and implementing effective environmental management strategies, the aluminum industry can work towards a more sustainable future. This commitment to sustainability not only benefits the environment but also supports economic growth and social well-being, ensuring a balanced approach to resource development.