Aluminium is one of the most widely used metals in the modern world, appearing in everything from aircraft and automobiles to packaging and construction materials. But how is aluminium made, and what processes transform raw ore into this lightweight yet durable metal?
Understanding how aluminium is made helps industries optimize material performance and gives insight into why aluminium remains essential across global manufacturing. In this comprehensive guide, we explain the aluminium production process step by step—from bauxite mining to recycling—while highlighting the role of alumina in aluminium manufacturing.
Where Does Aluminium Come From?
Although aluminium is the most abundant metal in the Earth’s crust, it is never found in its pure metallic form. Instead, aluminium exists naturally in bauxite, a reddish-brown ore rich in aluminum oxide (alumina).
Bauxite primarily contains aluminum hydroxide minerals such as gibbsite, boehmite, and diaspore, mixed with iron oxides, silica, and titanium dioxide. These impurities must be removed before aluminium metal can be produced.

📌 Image Placeholder: Bauxite mining and natural deposits
Step 1: Mining Bauxite
Bauxite is typically mined using open-pit mining techniques in tropical and subtropical regions such as Australia, Guinea, Brazil, and India.
Key Mining Considerations
- Removal of topsoil to access ore
- Transportation to refining facilities
- Environmental rehabilitation after mining
Sustainable mining practices are increasingly important to reduce ecological impact and ensure long-term resource availability.
Step 2: Refining Bauxite into Alumina (Bayer Process)
Before aluminium metal can be produced, bauxite must be refined into alumina (Al₂O₃) using the Bayer Process.
Bayer Process Explained
- Crushing and Grinding – Bauxite is crushed into a fine powder.
- Digestion – Mixed with hot sodium hydroxide, dissolving alumina.
- Clarification – Insoluble impurities settle out.
- Precipitation – Aluminum hydroxide crystals form.
- Calcination – Heating removes water, producing pure alumina powder.
Alumina is a critical industrial material with many applications beyond aluminium production. You can explore its broader industrial role in this guide on
👉 alumina versatile uses
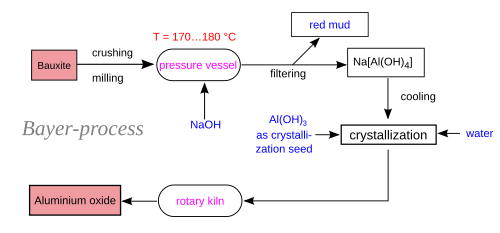
📌 Image Placeholder: Bayer process flow diagram
Step 3: Turning Alumina into Aluminium (Hall-Héroult Process)
Now comes the key step in answering how is aluminium made.
Alumina is converted into aluminium metal using electrolysis, specifically the Hall-Héroult Process.
Hall-Héroult Process Overview
- Alumina is dissolved in molten cryolite
- A powerful electric current separates aluminum from oxygen
- Molten aluminium collects at the bottom of the cell
- Aluminium is siphoned and cast into molds
⚡ This step is energy-intensive, which is why aluminium smelters are often located near low-cost power sources.
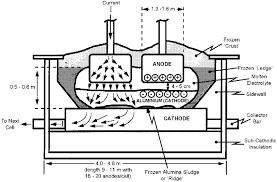
📌 Image Placeholder: Electrolytic aluminum smelting cells
Step 4: Casting and Fabrication
Once produced, molten aluminium is shaped into usable forms.
Common Casting Methods
- Ingot Casting – Large blocks for further processing
- Die Casting – Precision parts with complex shapes
Fabrication Techniques
- Rolling (sheets and foils)
- Extrusion (tubes and profiles)
- Forging (high-strength components)
These processes allow aluminium to be used in aerospace, construction, automotive, and packaging industries.
The Importance of Aluminium Recycling
One of aluminium’s greatest advantages is its 100% recyclability.
Recycling aluminium requires only 5% of the energy needed for primary production from bauxite, making it both economical and environmentally friendly.
Recycling Process
- Collection and sorting
- Shredding and cleaning
- Melting
- Recasting into new products
♻ Recycling reduces emissions, conserves natural resources, and supports sustainable manufacturing.
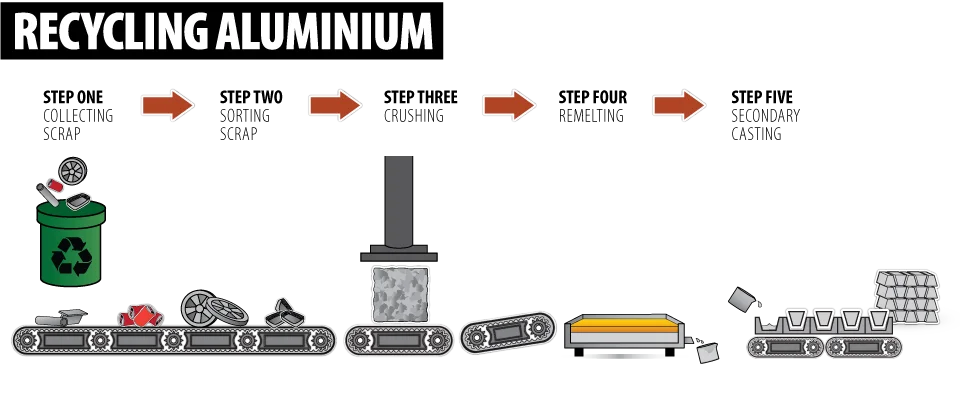
📌 Image Placeholder: Aluminum recycling process
Why Alumina Is Essential in Aluminium Production
Alumina acts as the critical intermediate between raw ore and finished metal. Beyond aluminium smelting, alumina is widely used in abrasives, ceramics, refractories, and advanced industrial applications.
Learn more about how alumina is applied across industries here:
👉 alumina versatile uses
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How is aluminium made from bauxite?
Aluminium is made by refining bauxite into alumina using the Bayer Process, then converting alumina into aluminium metal via electrolysis in the Hall-Héroult Process.
Why is aluminium not found in pure form in nature?
Aluminium reacts easily with oxygen, forming stable compounds like alumina, which is why it must be extracted through industrial processes.
What role does alumina play in aluminium production?
Alumina is the purified aluminum oxide extracted from bauxite and serves as the raw material for aluminium smelting.
Is aluminium production environmentally harmful?
Primary aluminium production is energy-intensive, but recycling significantly reduces environmental impact and energy consumption.
Why is aluminium recycling so important?
Recycling saves energy, reduces emissions, and preserves natural resources while maintaining the metal’s original properties.
Conclusion
So, how is aluminium made? The journey begins with bauxite mining, continues through alumina refining, and concludes with electrolysis and fabrication. Each stage plays a vital role in producing a metal that is lightweight, strong, recyclable, and indispensable to modern industry.
By understanding the aluminium production process—and the essential role of alumina—manufacturers and consumers alike can better appreciate the technology, efficiency, and sustainability behind this remarkable material.