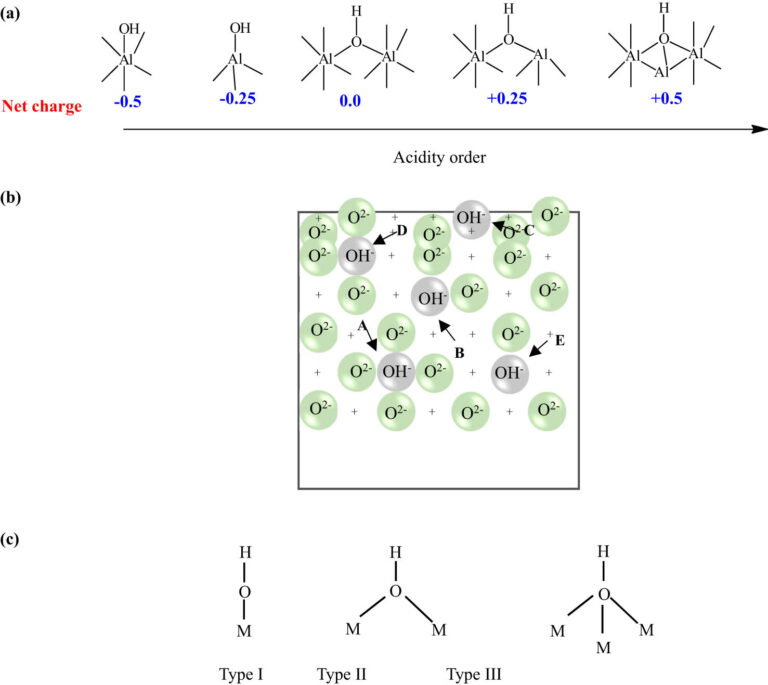
Aluminum refineries play a crucial role in the production of aluminum metal. They transform bauxite ore into alumina, a key material.
This process is known as alumina refining. It involves several complex steps, each vital to the final product’s quality.
The Bayer Process is the primary method used in these refineries. It efficiently extracts alumina from bauxite.
Alumina refineries are strategically located near bauxite mines. This reduces transportation costs and enhances efficiency.
In the USA, alumina refineries contribute significantly to the aluminum industry. They support both domestic and international markets.
Environmental considerations are increasingly important in refining operations. Efforts focus on reducing emissions and managing waste.
Technological advancements continue to improve the efficiency and sustainability of aluminum refineries. These innovations are crucial for the industry’s future.
What Is an Aluminum Refinery?
An aluminum refinery is an industrial plant. Its primary function is converting bauxite ore into alumina. This alumina is subsequently used to produce aluminum metal.
The refinery process involves several stages, each with specific machinery and technology. The stages are designed to extract the most alumina efficiently. These stages require precise chemical and mechanical processes.
Key features of an aluminum refinery include:
- Bauxite storage facilities
- Digestion units for chemical reactions
- Clarification and precipitation systems
- Calcination kilns for final heating
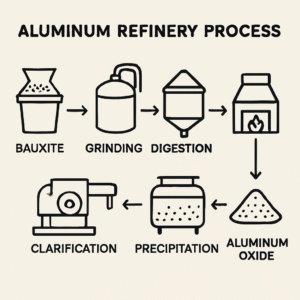
Aluminum refineries not only produce alumina. They also handle by-products like red mud, requiring proper disposal. The efficiency and design of these refineries determine the quality and cost-effectiveness of alumina production. Each refinery is meticulously planned to minimize energy use and maximize output.
The Importance of Alumina Refining
Alumina refining plays a crucial role in aluminum production. It acts as the link between raw bauxite and finished aluminum products. The process transforms bauxite into alumina, which is essential for aluminum manufacturing.
Without efficient alumina refining, aluminum production would face significant hurdles. The quality of alumina impacts the entire aluminum supply chain. Higher purity alumina ensures better aluminum quality and consistency.
Key reasons why alumina refining is important include:
- Facilitating aluminum production
- Enhancing aluminum product quality
- Reducing production costs through efficiency
- Supporting industries like automotive and aerospace
The refining process also provides an opportunity to manage environmental impact. By optimizing refining techniques, the industry can reduce waste and emissions, contributing to sustainability. As technology advances, the efficiency of alumina refining continues to improve.
Bauxite: The Starting Point
Bauxite is the primary raw material for aluminum production. It’s a naturally occurring ore rich in aluminum oxide. Before aluminum can be refined, bauxite must be mined and processed.
The quality of bauxite affects the efficiency and cost of alumina refining. High-quality bauxite ensures a smoother refining process. This leads to lower energy consumption and higher output.
Key components found in bauxite include:
- Aluminum hydroxides
- Iron oxides
- Silica
- Titanium dioxide

by Emmanuel Appiah (https://unsplash.com/@exappiah)
Mining bauxite involves extracting the ore from the earth’s crust. It is usually found in tropical and subtropical regions. The extraction process must be handled responsibly to protect the environment. The selection of high-quality bauxite is a critical step in ensuring efficient alumina refinery operations.
The Bayer Process: Core of Alumina Refining
The Bayer Process is central to the production of alumina. It was developed in 1888 by Karl Bayer. This process efficiently extracts aluminum oxide from bauxite.
The method involves four main stages. Each stage plays a vital role in ensuring purity and efficiency. Below, we delve into these key steps.
The process begins with digestion. Bauxite is mixed with caustic soda, heating to dissolve aluminum oxides.
Following digestion is clarification. This stage separates the impurities from the bauxite solution. The result is a clear sodium aluminate solution.
Next, precipitation occurs. Here, aluminum hydroxide crystals form as the solution cools. This reverses the initial reaction from digestion.
Finally, calcination takes center stage. The aluminum hydroxide is heated to produce alumina powder. This step creates the sought-after aluminum oxide.
Key stages of the Bayer Process include:
- Digestion
- Clarification
- Precipitation
- Calcination
by Growtika (https://unsplash.com/@growtika)

by Simon Takatomi (https://unsplash.com/@takatomi)
Each step requires precise control of conditions. Temperature, pressure, and chemical concentration are all crucial. Modern refinements have enhanced the Bayer Process’s efficiency, reducing energy consumption. The process remains the industry standard today.
Step 1: Digestion
The digestion phase begins with finely ground bauxite. It’s mixed with a hot caustic soda solution. The mixture is then heated under pressure in large vessels.
This heat and pressure dissolves the alumina from the bauxite. The reaction yields a sodium aluminate solution. This is a crucial initial step, laying the foundation for later stages.
by Europeana (https://unsplash.com/@europeana)
Step 2: Clarification
After digestion, the solution contains impurities. These must be removed to ensure high purity alumina.
Clarification involves settling and filtering out unwanted materials. The process leaves behind a clear sodium aluminate solution. This clarity is essential for the subsequent precipitation step.
Effective clarification is crucial. It prevents impurities from hindering the refining process. Clear solutions enhance the quality of the final alumina product.
Step 3: Precipitation
The cooled sodium aluminate solution undergoes precipitation. This phase reverses the initial digestion reaction.
As the solution cools, aluminum hydroxide crystals form. These crystals are then separated from the liquid. Precipitation effectively transforms dissolved aluminum into a solid form.
This step is vital for producing pure alumina. The process requires careful control of temperature and concentration. Precision ensures that the maximum amount of aluminum is recovered.
Step 4: Calcination
Calcination is the final step in the Bayer Process. It transforms aluminum hydroxide into aluminum oxide, also known as alumina.
The hydroxide crystals are heated in rotary kilns. This high-temperature treatment removes water, leaving behind alumina. The resulting alumina is a fine white powder, ready for smelting.
Calcination is energy-intensive but crucial. It generates the high-quality alumina used in various industries. The refined alumina is now fit for conversion into aluminum metal.
From Alumina to Aluminum: The Smelting Process
The journey from alumina to aluminum involves the Hall-Héroult process. This smelting technique is crucial for producing pure aluminum metal.
In this method, alumina is dissolved in molten cryolite. The mixture is then placed in an electrolytic cell. Here, direct current passes through, separating aluminum atoms from the oxygen.
The aluminum collects at the cathode, sinking to the bottom of the cell. This molten aluminum is periodically tapped and cast into ingots. The process is energy-intensive, demanding precise control over temperature and electricity.
Steps involved in smelting aluminum include:
- Dissolving alumina in cryolite
- Electrolytic reduction
- Collection of molten aluminum

by Michael (https://unsplash.com/@michael75)
The Hall-Héroult process has remained largely unchanged for over a century. However, ongoing innovations aim to improve efficiency and reduce environmental impact. Aluminum produced through this process finds applications across many industries, from automotive to aerospace.
Key Components of an Alumina Plant
An alumina plant is an intricate facility with several key components. Each part plays a significant role in refining bauxite into alumina. Efficient operation requires advanced machinery and skilled labor.
Key components of an alumina plant include:
- Crushers for size reduction of bauxite
- Digesters where bauxite is dissolved in sodium hydroxide
- Clarifiers for separating impurities
- Precipitators where alumina hydrate is precipitated from the solution
- Calciners to heat alumina hydrate, producing anhydrous alumina
These components work together in a carefully sequenced process. Efficient design and operation of these units are vital to ensure high-quality production and minimal environmental impact.

by Yoksel 🌿 Zok (https://unsplash.com/@yoksel)
Alumina Refineries in the USA
The USA is a prominent player in the global alumina market. Alumina refineries in the USA are strategically located to leverage domestic bauxite resources. These refineries support both local manufacturing and export markets.
Several key refineries operate in the USA:
- Point Comfort in Texas
- Gramercy Works in Louisiana
- Sherwin Alumina in Texas
These facilities contribute significantly to the country’s aluminum production capacity. They supply alumina to various industries, fostering economic growth and job creation.
Their strategic locations minimize transportation costs, enhancing efficiency. The USA’s alumina refineries also adhere to strict environmental regulations. These regulations ensure that operations are sustainable and environmentally friendly.
by Pin Adventure Map (https://unsplash.com/@pinadventuremap)
Environmental Considerations in Alumina Refining
Alumina refining has significant environmental impacts. It requires careful planning to reduce emissions and waste. Refineries worldwide strive to adopt sustainable practices.
Efforts to minimize environmental effects focus on several areas:
- Reducing greenhouse gas emissions
- Managing red mud waste effectively
- Conserving water resources
Innovations in technology are helping to lessen these impacts. New methods improve efficiency and decrease waste production. This is crucial for meeting environmental regulations.
Environmental performance is vital for the industry’s sustainability. Refineries work under strict guidelines to protect ecosystems. Compliance with these standards ensures long-term viability and community support.

by Sebastien Devocelle (https://unsplash.com/@lecelle)
Technological Innovations and Industry Trends
Technological advances continue to transform alumina refining. Efficiency is improving, and environmental impacts are decreasing. These innovations are crucial for sustainability and competitiveness.
Key trends shaping the industry include:
- Automation and digital technologies
- Energy-efficient processes
- Carbon capture and storage methods
These developments not only reduce costs but also enhance refinery performance. Automation increases precision and reduces human error. Energy-efficient solutions lower consumption and emissions.
Staying ahead requires embracing new technologies. Refineries that invest in innovation gain a competitive edge. The focus is on sustainable practices that meet global demand and regulatory standards.

by J Loren Norris (https://unsplash.com/@jlorennorris)
Economic Impact and Global Market Dynamics
The alumina refining industry plays a crucial role in the global economy. It fuels numerous sectors, such as automotive, aerospace, and construction. The demand for aluminum continues to grow globally, pushing refineries to meet extensive supply needs.
Key economic factors affecting the market include:
- Global demand fluctuations
- Raw material price volatility
- International trade regulations
Alumina refineries must navigate these dynamics to remain profitable. As one of the industry’s players, the USA contributes significantly through exports. Strategic positioning and innovation help refineries stay competitive. As the market evolves, they must adapt quickly to sustain their economic impact.

by Joshua Olsen (https://unsplash.com/@photowolf)
Challenges and the Future of Alumina Refining
Alumina refining faces several challenges today. Resource scarcity and tightening regulations demand innovation. Refineries must evolve to remain viable in a competitive landscape.
Ongoing challenges include:
- Regulatory compliance with environmental standards
- Technological upgrades to reduce energy consumption
- Managing by-products like red mud
The industry’s future hinges on sustainability and efficiency. Embracing renewable energy and advanced technology is pivotal. Companies focus on reducing emissions and enhancing recycling efforts.
Strategic partnerships and research continue to shape refinements in the process. The industry’s future is intertwined with global sustainability goals. By adopting these forward-looking strategies, the alumina refining sector can thrive.

by Alexander Psiuk (https://unsplash.com/@alexdeloy)
Conclusion: The Role of Alumina Refineries in Modern Industry
Alumina refineries are essential in transforming raw bauxite into usable aluminum. This process supports many industries like automotive and aerospace. Their role is vital in the global economy.
The continuous innovation and commitment to sustainability make them key players. As industries evolve, alumina refineries must adapt too. They ensure efficient and eco-friendly production. Through them, the modern world benefits from aluminum’s versatile applications. Their impact on industrial growth and development is significant.