When it comes to materials used in engineering and manufacturing, alumina is a standout for its impressive properties. But what exactly is the tensile strength of alumina, and why is it so important? In this article, we will delve into the concept of tensile strength, explore why alumina is a preferred material, and examine its applications across various industries.
Tensile strength is a measure of the force required to pull something to the point where it breaks. It is a critical factor in determining a material’s ability to withstand tension without failing. Essentially, it tells us how much pulling force a material can handle before it starts to tear apart. Understanding tensile strength is vital for engineers and designers who seek to choose the right materials for specific applications.
The Importance of Tensile Strength in Material Selection
Tensile strength is one of the primary considerations in material selection for engineering applications. It informs engineers about the suitability of a material for structures that will experience tensile loads. High tensile strength materials are preferred for applications that require durability and reliability under stress. This parameter helps in avoiding material failure that could lead to catastrophic consequences in structural applications.
The Role of Tensile Strength in Product Design
In product design, tensile strength plays a crucial role in ensuring that the final product can withstand operational stresses. Designers must account for tensile strength to prevent material deformation or failure over time. By understanding the tensile limits, designers can make informed decisions about material thickness, shape, and overall design to optimize performance. This is particularly important in industries like aerospace and automotive, where safety and reliability are paramount.
How is Tensile Strength Measured?
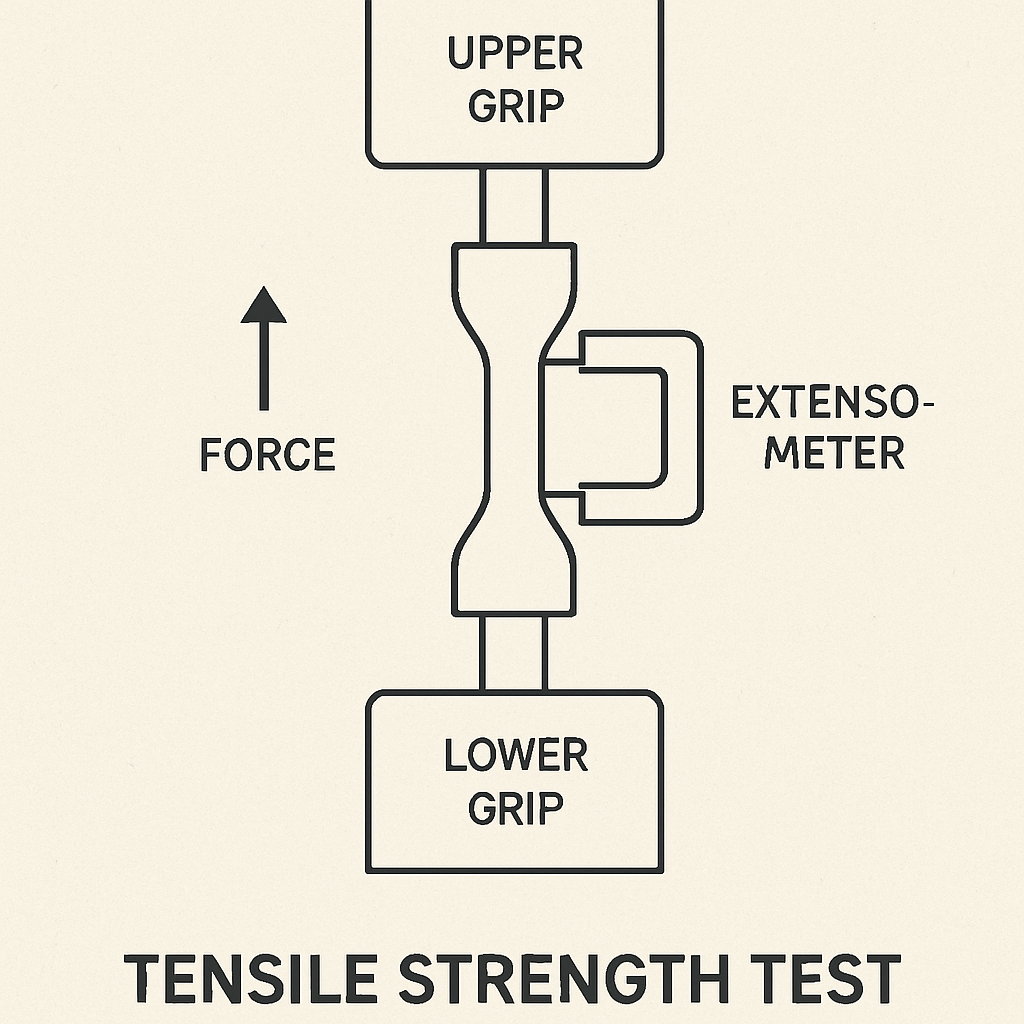
Tensile strength is measured using a tensile test. During the test, a sample material is stretched until it fractures. The maximum stress the material can withstand while being stretched is recorded as its tensile strength. The result is expressed in units like megapascals (MPa) or pounds per square inch (psi). This method provides a clear picture of the material’s capacity to handle stress, which is essential for evaluating its suitability for specific applications.
The Process of Conducting a Tensile Test
The tensile test involves a controlled environment where the material sample is subjected to a gradually increasing pulling force. The sample is often in a standardized shape to ensure consistency in results. As the force increases, the material elongates until it reaches its breaking point. The data collected during the test, such as elongation and ultimate tensile strength, provides insights into the material’s mechanical properties.
Analyzing Tensile Test Results
After conducting a tensile test, the results are analyzed to determine the material’s performance characteristics. Key metrics include the material’s yield strength, ultimate tensile strength, and elongation at break. These metrics help in understanding how the material behaves under stress and can guide decisions on its potential applications. Engineers use this data to predict how the material will perform in real-world scenarios.
Alumina: An Overview

Alumina, also known as aluminum oxide (Al2O3), is a white or nearly colorless crystalline substance. It is derived from bauxite ore and is known for its high hardness and thermal stability. These properties make alumina an excellent choice for a wide range of industrial applications. Its ability to maintain structural integrity in harsh environments makes it indispensable in various fields.
The Manufacturing Process of Alumina
The production of alumina from bauxite ore involves several steps. Initially, the bauxite is mined and then refined through the Bayer process. This involves dissolving bauxite in sodium hydroxide, which separates alumina from impurities. The alumina is then precipitated, washed, and calcined to remove water, resulting in pure aluminum oxide. This method ensures high purity and quality of the final product.
Properties of Alumina
Alumina is valued for its:
- High hardness: Alumina is one of the hardest materials known, making it extremely resistant to wear and abrasion. This property is crucial for applications that involve constant friction or impact.
- Thermal stability: It retains its strength and rigidity at high temperatures, which is crucial for applications in high-temperature environments. This makes alumina ideal for use in furnaces and kilns.
- Corrosion resistance: Alumina is resistant to chemical attack, which makes it durable and long-lasting. This resistance extends the lifespan of products made from alumina, reducing maintenance needs.
Variants and Grades of Alumina
Alumina comes in different grades and forms, tailored for specific applications. Variants like tabular alumina, reactive alumina, and calcined alumina have distinct properties that suit different industrial requirements. Each variant is engineered to enhance certain attributes, such as purity or particle size, to meet the demands of various applications.
Tensile Strength of Alumina
The tensile strength of alumina is one of the key factors that contribute to its widespread use in various industries. Generally, alumina’s tensile strength ranges from 300 MPa to 600 MPa. This range can vary depending on the purity and specific manufacturing processes used to produce the alumina. Understanding these variations helps manufacturers and engineers choose the right type of alumina for their needs.
Factors Affecting Alumina Tensile Strength
Several factors can influence the tensile strength of alumina:
- Purity: Higher purity alumina tends to have higher tensile strength due to fewer impurities that can act as points of weakness. Impurities can create stress concentration points that reduce material integrity.
- Grain size: Finer grains in the material can improve tensile strength, as they enhance the material’s overall density and uniformity. Smaller grains lead to a more compact microstructure, which contributes to increased strength.
- Sintering process: The method and temperature used in the sintering process can affect the microstructure of the alumina, impacting its tensile strength. Optimal sintering conditions ensure that the grains are properly bonded, maximizing tensile strength.
Enhancements in Alumina Tensile Strength
Advancements in technology have allowed for significant improvements in the tensile strength of alumina. Techniques such as doping with certain elements can enhance its strength and other properties. Innovations in processing, like advanced sintering techniques, have also contributed to higher performance alumina products.
Comparative Analysis with Other Materials
Alumina’s tensile strength is often compared to that of other ceramics and metals. While metals may offer higher ductility, alumina’s combination of strength and thermal resistance offers advantages in specific scenarios. Comparing these properties helps industries choose between different materials based on the specific needs of their applications.
Applications of Alumina
by Harper Sunday (https://unsplash.com/@harpersunday)
Thanks to its impressive tensile strength and other favorable properties, alumina is used in a variety of applications. Its versatility and reliability make it a preferred choice across multiple sectors. Understanding its applications helps industries maximize its potential.
Industrial Applications
- Cutting tools: Alumina is used in the manufacture of cutting tools due to its hardness and durability. This ensures long-lasting performance even under high-stress machining conditions.
- Electrical insulators: Its insulating properties make alumina suitable for electrical insulators in high-voltage applications. Alumina’s ability to withstand electric fields without breaking down ensures safety and reliability.
- Wear-resistant coatings: Alumina coatings are applied to surfaces that need protection from wear and corrosion. These coatings extend the life of machinery and equipment, reducing maintenance costs.
Medical Applications
- Prosthetics: Alumina is used in joint replacements and dental prosthetics due to its biocompatibility and strength. This ensures that prosthetics are both durable and safe for human use.
- Surgical instruments: Its high tensile strength and resistance to sterilization processes make alumina ideal for surgical tools. This ensures that instruments maintain their integrity and performance even after repeated sterilization cycles.
Emerging Applications of Alumina
As technology progresses, new applications for alumina are emerging. In the field of electronics, alumina is being explored for use in semiconductors and microelectronics. Its thermal conductivity and electrical insulation properties make it an attractive candidate for these advanced applications.
Advantages and Limitations of Using Alumina
Understanding the benefits and drawbacks of using alumina is essential for making informed decisions about its application. By weighing these factors, industries can effectively incorporate alumina into their products and processes.
Advantages
- Durability: Alumina’s hardness and resistance to wear make it long-lasting, reducing the need for frequent replacements. This contributes to cost savings over time.
- Versatility: Its ability to withstand high temperatures and corrosion broadens the scope of its applications. This versatility makes alumina a go-to material for challenging environments.
Limitations
- Brittleness: While alumina is strong, it is also brittle, which means it can fracture under sudden impacts or extreme stress. This limits its use in applications where impact resistance is crucial.
- Cost: High-purity alumina can be expensive to produce, affecting its overall cost-effectiveness in certain applications. Industries must balance the benefits of alumina against its production costs.
Strategies for Overcoming Limitations
To address the limitations of alumina, researchers and engineers are exploring composite materials that combine alumina with other substances. These composites aim to enhance toughness while retaining the favorable properties of alumina. Additionally, advancements in manufacturing techniques are working towards reducing production costs.
Conclusion
Understanding the tensile strength of alumina is crucial for industries that rely on this material for its durability and performance. Its high tensile strength, combined with other properties like hardness and thermal stability, makes it an invaluable resource in both industrial and medical fields. However, considerations such as brittleness and cost must also be factored into decisions regarding its use. As technology advances, the potential for alumina’s applications will likely expand, offering even more opportunities to harness its unique properties.
By knowing more about the tensile strength of alumina, businesses can make informed decisions about incorporating this robust material into their products and processes, ensuring durability and reliability in their applications. This knowledge empowers industries to innovate and improve products, ultimately leading to better performance and customer satisfaction.