Alumina stone is a fascinating material with unique properties and a wide range of applications. Whether you’re a craftsman, a scientist, or simply curious about materials, understanding alumina stone can offer valuable insights. In this article, we’ll explore what makes alumina stone so special, its uses, and how to work with it effectively.
Alumina stone, also known as aluminum oxide stone, is primarily composed of aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃). This compound is one of the hardest materials available, second only to diamond. Because of its hardness, alumina stone is highly resistant to wear and corrosion, making it ideal for a variety of industrial and domestic uses.
For more on its versatile applications, check out our guide on alumina versatile uses.
Composition and Characteristics
The primary component of alumina stone is aluminum oxide, which gives it its distinctive hardness and durability. This composition also makes it resistant to high temperatures and chemical reactions, allowing it to maintain its integrity in extreme conditions.
- Hardness: Alumina stone is incredibly hard, providing excellent wear resistance. This makes it particularly useful in industries where materials are exposed to abrasive conditions.
- Durability: It can withstand significant physical and chemical stress without degrading. This resistance to stress ensures that products made from alumina stone have a long lifespan, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
- Heat Resistance: It remains stable even at high temperatures, which is crucial for many industrial applications. Its ability to maintain structural integrity at extreme temperatures makes it invaluable in environments like metalworking and glassmaking.
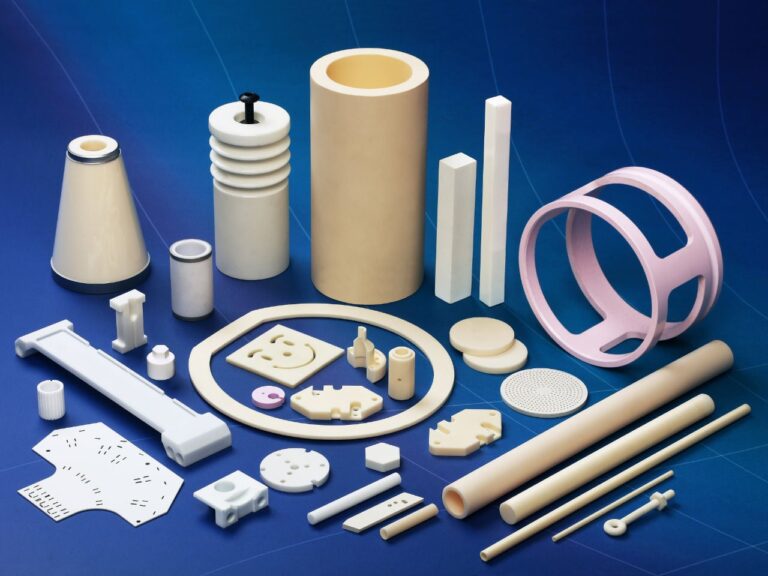
Varieties and Grades of Alumina Stone
Alumina stones come in different forms, including natural stones, synthetic stones, and various grits and grades, depending on their specific use.
- Natural vs. Synthetic: Natural alumina stones are often used in applications where a natural finish is desired, whereas synthetic stones are preferred in industrial settings due to their uniformity and predictability.
- Grit and Grade: The grit of an alumina stone determines its level of abrasiveness. Coarser grits are used for heavy-duty grinding, while finer grits are used for polishing and finishing tasks.
- Customization: Some industries require specialized alumina stones that are custom-cut or shaped to fit specific machinery or tools, enhancing efficiency and precision.

Historical Context of Alumina Stone
Understanding the historical context of alumina stone can provide insight into its current applications and future potential.
- Discovery and Development: The discovery of aluminum oxide’s properties dates back several centuries, but it wasn’t until the 20th century that its potential was fully realized.
- Industrial Revolution: The industrial revolution spurred the development of synthetic production methods, allowing for wider use across various sectors.
- Modern Advances: Technological advances have continued to enhance the quality and applicability of alumina stone, making it a staple in modern manufacturing processes.
Applications of Alumina Stone
Alumina stone is used in a variety of fields due to its robust properties. Here are some of the most common applications:
Industrial Applications
In the industrial sector, alumina stone is used for:
- Grinding and Polishing: Due to its hardness, alumina stone is ideal for grinding and polishing metals and other materials. Tools like the “alumina-based stone shapton” are popular in industries requiring precision. The stones maintain sharpness over time, ensuring consistent performance in high-demand environments.
- Cutting Tools: It is often used to manufacture cutting tools that require a sharp, durable edge. These tools are essential in manufacturing processes where precision cutting is necessary, such as in the production of automotive parts and aerospace components.
- Ceramics and Refractories: Its heat resistance makes it suitable for high-temperature environments, such as kilns and furnaces. Alumina stone‘s ability to withstand extreme heat without breaking down ensures longevity and reliability in ceramic production.
For more about alumina stone’s uses in industries, visit our full alumina guide.

Craft and Hobby Use
For artisans and hobbyists, alumina stone is prized for:
- Jewelry Making: It’s used in polishing gemstones, such as lapis lazuli. If you’re wondering how to polish lapis stone with alumina, the process involves using alumina-based polishing compounds to achieve a high shine. This high-shine finish is vital for enhancing the visual appeal of jewelry pieces.
- Sharpening Stones: Many sharpening stones are made from alumina, providing a reliable and efficient way to maintain blades. These stones are favored by chefs and craftsmen alike for their ability to produce a razor-sharp edge on knives and tools.
- Sculpture and Design: Artists use alumina stone to carve intricate designs, benefiting from its hardness and ability to hold fine details. This is particularly useful in creating sculptures that require durability and precision.
Scientific and Medical Uses
In scientific and medical fields, alumina stone‘s properties are leveraged for:
- Laboratory Equipment: Its resistance to chemical reactions makes it perfect for lab settings. Lab equipment made from alumina stone can withstand corrosive substances, ensuring safety and reliability in experiments.
- Medical Implants: Its biocompatibility allows it to be used in certain types of medical implants. Alumina’s compatibility with the human body reduces the risk of rejection, making it a preferred material for joint replacements and dental implants.
- Research Applications: Alumina’s unique properties make it a subject of study in materials science, helping researchers develop new technologies and improve existing processes.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions about Alumina Stone
Q1: What is the main component of alumina stone?
A1: The primary component of alumina stone is aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃), which gives it its hardness, durability, and heat resistance.
Q2: What are the main applications of alumina stone?
A2: Alumina stone is used in a wide range of applications, including grinding, polishing, cutting tools, ceramics, refractories, jewelry making, and even medical implants.
Q3: How do I work with alumina stone for sharpening?
A3: To work with alumina stone for sharpening, choose the right grit size, use water or oil for lubrication, and apply consistent pressure to avoid uneven wear.
Q4: Is alumina stone environmentally friendly?
A4: Yes, alumina stone is non-toxic and environmentally friendly, making it an excellent choice for sustainable practices in various industries.
Working with Alumina Stone
To make the most of alumina stone, it’s important to understand how to work with it effectively. Here are some tips:
Polishing and Sharpening
- Choose the Right Grade: Depending on your project, select the appropriate grit size for your alumina stone. Coarse grits are better for shaping, while finer grits are ideal for finishing.
- Use Water or Oil: For sharpening, use water or oil to lubricate the stone, which helps to remove metal particles and maintain the stone’s effectiveness.
- Consistent Pressure: Apply consistent pressure to avoid uneven wear and ensure a uniform finish.
Maintenance and Care
- Clean Regularly: After each use, clean your alumina stone to remove any debris or residue. Regular cleaning helps maintain its effectiveness and longevity.
- Store Properly: Keep your stones dry and store them in a stable environment to avoid damage or degradation.
- Inspection: Periodically inspect your alumina stone for signs of wear or damage to extend its life.
Benefits of Using Alumina Stone
Alumina stone offers several advantages, making it a preferred choice in many applications:
- Longevity: Its durability means it lasts longer than many other materials, providing value for money.
- Versatility: From industrial to artistic applications, alumina stone‘s versatility is unmatched.
- Precision: Its consistent performance ensures precision in tasks like sharpening and polishing.
Conclusion
Alumina stone is a remarkable material with properties that make it indispensable across various industries and crafts. Its hardness, durability, and versatility are unmatched, making it a valuable asset for anyone working with materials that require precision and resilience. Whether you’re using it for industrial purposes or artistic endeavors, understanding how to work with alumina stone will enhance your projects and outcomes.
By following the guidelines on proper use and maintenance, you can maximize the benefits of alumina stone and ensure that it serves you well for years to come.


