Aluminium oxide, commonly known as alumina, is a compound of aluminium and oxygen with the chemical formula Al₂O₃. This compound exists in several crystalline forms, with sapphire being one of the most renowned. Sapphire, in its purest form, is a colorless and transparent crystal, but it can exhibit a range of colors depending on the presence of trace impurities. This article delves into the multifaceted properties of aluminium oxide sapphire, emphasizing its unique benefits and applications across various industries. Understanding these properties enhances our appreciation of sapphire’s role in advancing technology and industry.
Structural and Physical Properties
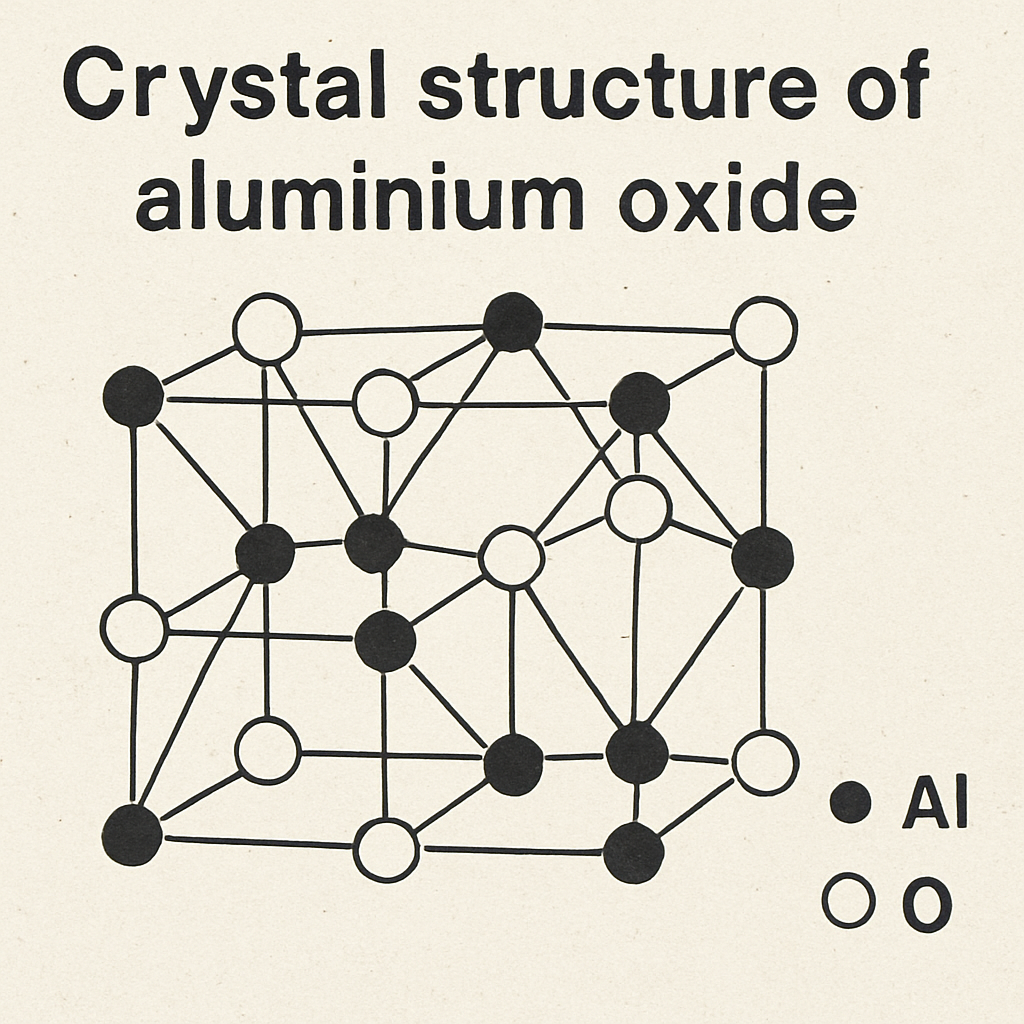
The remarkable properties of aluminium oxide sapphire stem from its crystalline structure. The hexagonal lattice is robust, contributing to sapphire’s exceptional hardness, second only to diamond on the Mohs scale. This hardness makes it an ideal material for applications requiring durability and resistance to scratching and wear. Additionally, the high melting point of approximately 2,072°C highlights its thermal stability, making it suitable for high-temperature environments.
Hardness and Durability
Aluminium oxide sapphire’s hardness is a defining characteristic. This makes it an excellent choice for scratch-resistant surfaces, such as watch faces and electronic device screens. The material’s durability ensures that it remains unscathed in environments that would damage lesser materials. Furthermore, sapphire’s resistance to abrasion extends its lifespan in industrial applications, reducing the frequency of replacements and maintenance.
Thermal Stability
The high melting point of sapphire is indicative of its thermal stability. This property is crucial in applications involving high temperatures, such as furnaces and engines. Sapphire’s ability to withstand extreme temperatures without losing structural integrity is unmatched by many other materials. Additionally, its thermal stability allows it to maintain clarity and strength, even when subjected to rapid temperature changes.
Mechanical Strength
Sapphire boasts impressive mechanical strength, which is vital for applications requiring robust materials. Its resistance to mechanical stress makes it suitable for aerospace and defense applications, where mechanical failure is not an option. The material’s strength also contributes to its use in protective coatings, providing a resilient barrier against physical impacts and environmental factors.
Optical Properties
Aluminium oxide sapphire exhibits extraordinary optical properties, which are pivotal in its application in optics and electronics. It is optically transparent over a wide range of wavelengths, from ultraviolet to infrared, rendering it invaluable for lenses and windows in high-performance optical systems. Furthermore, the birefringent nature of sapphire allows it to polarize light, which is essential in certain optical applications.

Transparency Across Wavelengths
Sapphire’s optical transparency is a key asset in various optical technologies. It allows for the passage of light without significant absorption or distortion, making it ideal for high-precision optical instruments. This property is particularly beneficial in environments requiring high clarity and minimal interference. Its transparency across a broad spectrum also supports advancements in imaging and photonics technologies.
Birefringence and Polarization
The birefringent nature of sapphire enhances its utility in optical systems. Birefringence refers to the material’s ability to split light into two distinct paths, which is critical in polarization applications. This property is harnessed in devices that require control over light’s polarization, such as lasers and optical modulators. As such, sapphire is indispensable in the development of advanced optical components and systems.
Light Transmission and Reflection
Sapphire’s ability to efficiently transmit and reflect light is crucial in optical design. Its low reflectivity and high transmission rates ensure that light passes through with minimal loss. This makes it an ideal choice for lenses and windows in high-performance optical equipment. Additionally, sapphire’s reflection properties are exploited in designing optical coatings that enhance performance and reduce glare.
Electrical Properties
In the realm of electronics, sapphire’s electrical properties are equally significant. It serves as an excellent electrical insulator with a dielectric constant of approximately 9.4, which makes it ideal for use as a substrate in microelectronic devices. Its low dielectric loss and high dielectric strength contribute to the miniaturization of components, enhancing the performance and efficiency of electronic devices.
Dielectric Constant and Insulation
Sapphire’s dielectric constant is a measure of its insulating capability. It prevents electrical currents from passing through, making it perfect for protecting sensitive electronic components. This property is crucial in microelectronic devices, where precise insulation is necessary to prevent short circuits and maintain device integrity. The material’s insulating properties are leveraged in a variety of advanced electronic applications.
Dielectric Loss and Strength
The low dielectric loss of sapphire is advantageous in electronic applications. This means that minimal energy is lost as heat, preserving the efficiency of electronic systems. High dielectric strength further enhances its utility, allowing it to withstand high voltages without breaking down. These properties enable the design of compact, high-performance electronic devices that are more reliable and efficient.
Role in Miniaturization
Sapphire’s electrical properties play a pivotal role in the miniaturization of electronic components. As devices become smaller, the need for materials that can support high performance in limited spaces becomes critical. Sapphire’s insulating capabilities and thermal properties allow for the development of smaller, more efficient devices. This is especially important in the production of advanced microchips and sensors.
Chemical Properties and Stability
Aluminium oxide sapphire is chemically inert and exhibits excellent resistance to chemical attack. This resistance is crucial in environments where exposure to harsh chemicals is prevalent. Its stability in both acidic and basic conditions ensures longevity and reliability in diverse applications, from chemical processing to protective coatings.
Resistance to Chemical Attack
Sapphire’s chemical resistance is a valuable property in harsh environments. It remains unaffected by most acids, bases, and solvents, making it ideal for use in chemical processing equipment. This resistance ensures that components maintain their integrity and functionality, even when exposed to corrosive substances. It is also used in protective coatings for surfaces that encounter chemical exposure.
Stability in Extreme Conditions
The stability of sapphire under extreme chemical conditions is unmatched. It maintains its structural integrity and performance in both acidic and basic environments. This makes it suitable for applications in chemical plants, laboratories, and industrial settings where exposure to extreme substances is common. The material’s stability ensures long-term reliability and safety in these demanding conditions.
Longevity and Reliability
Sapphire’s chemical properties contribute to its longevity and reliability in various applications. Its resistance to degradation ensures that components and devices last longer, reducing the need for frequent replacements. This longevity is particularly important in industries where downtime and maintenance costs must be minimized. Sapphire’s reliability enhances the performance and cost-effectiveness of equipment in demanding environments.
Thermal Conductivity
The thermal conductivity of sapphire is another noteworthy property, with values significantly higher than those of other insulating materials. This characteristic is particularly advantageous in thermal management applications, where efficient heat dissipation is crucial. Sapphire’s ability to conduct heat effectively while maintaining electrical insulation is exploited in high-power electronic devices to prevent overheating and ensure optimal performance.
Efficient Heat Dissipation
Sapphire’s high thermal conductivity allows for efficient heat dissipation in electronic devices. This property is crucial in preventing overheating and ensuring consistent performance. In high-power applications, such as power electronics and LED lighting, sapphire’s ability to manage heat improves device reliability and lifespan. Efficient heat dissipation is a key factor in the design of advanced electronic systems.
Thermal Management in Electronics
In electronics, thermal management is critical for maintaining device performance and longevity. Sapphire’s thermal properties allow it to effectively manage and distribute heat. This prevents thermal hotspots, which can damage components and reduce efficiency. Sapphire’s role in thermal management is vital in the development of compact, high-performance electronic devices that require precise temperature control.
Balance of Conductivity and Insulation
The unique balance of thermal conductivity and electrical insulation makes sapphire ideal for electronic applications. It conducts heat away from sensitive components while providing electrical insulation, ensuring device safety and efficiency. This balance is leveraged in the design of advanced electronic systems that require both thermal and electrical management. Sapphire’s properties support the development of innovative technologies and devices.
Applications Across Industries
The unique combination of properties exhibited by aluminium oxide sapphire has led to its widespread use across numerous industries. Below, we explore some of the most prominent applications:
Electronics and Semiconductors
In the semiconductor industry, sapphire’s role as a substrate for silicon-on-sapphire (SOS) technology cannot be overstated. This technology enhances the performance of integrated circuits by reducing parasitic capacitance and improving radiation hardness. Moreover, its use in light-emitting diodes (LEDs) is pivotal, as sapphire substrates allow for efficient light emission and thermal management.
Role in Integrated Circuits
Sapphire substrates play a crucial role in the development of integrated circuits. They provide a stable and reliable platform that enhances circuit performance and efficiency. The reduction of parasitic capacitance improves signal integrity and speed, making sapphire a preferred material in advanced semiconductor technologies. This application is instrumental in the production of high-performance computing and communication devices.
Advancements in LED Technology
The use of sapphire in LED technology has revolutionized lighting solutions. Sapphire substrates enable efficient light emission and heat management, resulting in brighter and more energy-efficient LEDs. This has significant implications for lighting in residential, commercial, and industrial applications. The advancements in LED technology underscore sapphire’s impact on energy efficiency and sustainability.
Radiation Hardness in Electronics
Sapphire’s radiation hardness is a critical property in the design of electronic devices used in harsh environments. It ensures that components can withstand radiation exposure without degradation. This is particularly important in aerospace, military, and space applications, where electronic systems must operate reliably under extreme conditions. Sapphire’s contribution to radiation-hardened electronics enhances the safety and longevity of critical technologies.
Optics and Aerospace
Sapphire’s optical transparency and durability make it a material of choice for aerospace applications. It is used in windows, sensors, and lenses that require resistance to extreme conditions. The aerospace industry capitalizes on sapphire’s ability to withstand high temperatures and mechanical stress, ensuring reliability and longevity in critical components.

by Matias Luge (https://unsplash.com/@matiasluge)
Optical Systems in Aerospace
In aerospace, sapphire is integral to the development of advanced optical systems. Its transparency and durability ensure that optical sensors and instruments perform reliably in harsh environments. Sapphire’s resistance to temperature fluctuations and mechanical stress is crucial for maintaining optical clarity and accuracy. These systems are essential for navigation, communication, and surveillance in aerospace applications.
Structural Components and Windows
Sapphire’s mechanical strength and thermal stability make it ideal for structural components and windows in aerospace. It can withstand the extreme temperatures and pressures experienced during flight, maintaining integrity and safety. Sapphire windows provide clarity and protection in cockpit displays and observation ports. Its use in structural components enhances the durability and performance of aerospace vehicles.
Sensors and Instrumentation
Sapphire is widely used in sensors and instrumentation for aerospace applications. Its optical and thermal properties support the development of high-performance sensors that operate reliably in extreme conditions. These sensors are critical for monitoring and controlling aerospace systems, ensuring safety and efficiency. Sapphire’s contribution to sensor technology is vital for the advancement of aerospace instrumentation.
Medical and Industrial Applications
In the medical field, sapphire’s biocompatibility and wear resistance are harnessed in surgical instruments and implants. Its chemical inertness and ability to withstand sterilization processes make it ideal for use in medical environments. Additionally, in industrial settings, sapphire is employed as a protective layer in machinery and equipment exposed to abrasive conditions, extending their lifespan and reducing maintenance costs.
Biocompatibility in Medical Devices
Sapphire’s biocompatibility is a key advantage in medical applications. It is non-reactive and safe for use in surgical instruments and implants, reducing the risk of adverse reactions. Its wear resistance ensures that medical devices perform reliably over time, even in demanding conditions. Sapphire’s role in medical technology enhances patient safety and device longevity.
Surgical Instruments and Implants
In surgical applications, sapphire is valued for its strength and precision. It is used to manufacture surgical instruments that require sharpness and durability. Sapphire implants offer long-term reliability and compatibility with the human body. These properties are essential for improving surgical outcomes and patient care in medical settings.
Industrial Equipment and Machinery
Sapphire’s wear resistance and chemical stability are exploited in industrial applications. It serves as a protective layer for machinery and equipment exposed to harsh conditions, extending their operational life. This reduces maintenance costs and downtime, improving productivity and efficiency in industrial operations. Sapphire’s contribution to industrial equipment enhances performance and cost-effectiveness.
Environmental and Economic Considerations
While the benefits of aluminium oxide sapphire are undeniable, it is essential to consider the environmental and economic implications of its production and use. The extraction and processing of raw materials for sapphire production can have environmental impacts, necessitating sustainable practices and innovations in recycling and reuse.
Sustainable Production Practices
The environmental impact of sapphire production highlights the need for sustainable practices. This includes minimizing waste, reducing energy consumption, and using eco-friendly materials in manufacturing processes. Innovations in recycling and reuse of sapphire materials can further mitigate environmental impacts. Sustainable production practices ensure that the benefits of sapphire are realized without compromising the environment.
Innovations in Recycling and Reuse
Recycling and reuse of sapphire are critical for reducing environmental impact. Developing efficient recycling methods allows for the recovery of valuable materials and reduces the demand for raw extraction. Reuse of sapphire in various applications extends its lifecycle and minimizes waste. Innovations in recycling and reuse contribute to the sustainability of sapphire production and use.
Economic Impact
Economically, the high cost of sapphire production is a consideration for industries evaluating its adoption. However, the long-term benefits of durability, performance, and reduced maintenance can offset the initial investment, particularly in applications where material failure can result in significant costs. The economic impact of sapphire is positive in industries that value reliability and performance.
Conclusion
The exploration of aluminium oxide sapphire reveals a material of unparalleled versatility and utility. Its unique properties, including exceptional hardness, optical clarity, and chemical stability, position it as an indispensable material across a multitude of industries. As technology advances and the demand for high-performance materials increases, the role of aluminium oxide sapphire will undoubtedly continue to expand, driven by innovations that leverage its remarkable properties.
In conclusion, the study of aluminium oxide sapphire underscores the importance of this material in modern technology and industry. Its contributions to advancements in electronics, optics, aerospace, and medicine exemplify the transformative impact of materials science in shaping the future. The ongoing exploration and innovation in the use of sapphire will continue to drive progress and open new possibilities across diverse fields.