Aluminum oxide is a compound that you encounter in various forms every day, even if you don’t realize it. From the manufacturing of aluminum metal to its role in ceramics and glass production, aluminum oxide is essential in many industries. But what exactly is aluminum oxide, and how is it formed? Let’s dive into the world of chemistry to understand its chemical formula and significance.
What is Aluminum Oxide?
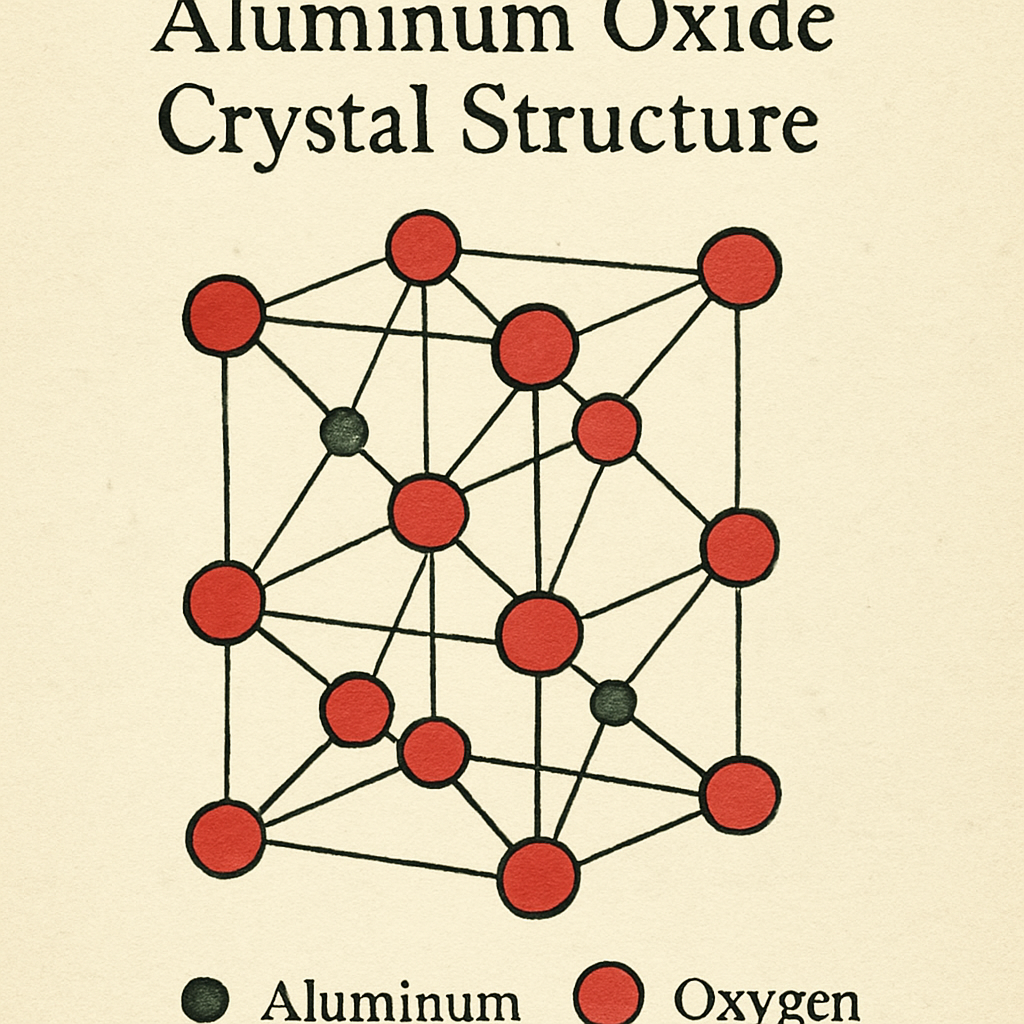
Aluminum oxide, also known as alumina, is a chemical compound made up of aluminum and oxygen. Its chemical formula is Al₂O₃. This compound is a white, powdery substance that is highly stable and resistant to corrosion. It is commonly found in nature in the form of bauxite ore, which is the primary source of aluminum.
The Composition of Aluminum Oxide
The chemical formula Al₂O₃ tells us that each molecule of aluminum oxide consists of two aluminum (Al) atoms and three oxygen (O) atoms. This ratio is essential for its stability and properties. The formula indicates how these elements are bonded together to form a compound. The aluminum atoms donate electrons to the oxygen atoms, creating a stable ionic structure. This bonding structure gives aluminum oxide its characteristic properties, such as high melting point and hardness.
The Nature of Aluminum
Aluminum is a lightweight metal known for its strength and resistance to corrosion. In aluminum oxide, aluminum plays a crucial role in providing structural integrity. The two aluminum atoms in Al₂O₃ form strong ionic bonds with the oxygen atoms, resulting in a compound that is both durable and versatile. This interaction is vital for the compound’s ability to withstand extreme conditions without degrading.
The Role of Oxygen in Al₂O₃
Oxygen, a highly electronegative element, plays a fundamental role in the formation of aluminum oxide. Its ability to attract electrons from aluminum atoms facilitates the creation of stable ionic bonds. The presence of three oxygen atoms ensures a complete and balanced structure, which contributes to the compound’s chemical inertness and resistance to environmental factors.
How is Aluminum Oxide Formed?
Aluminum oxide forms when aluminum reacts with oxygen. This reaction can occur naturally or be induced in an industrial setting.
Natural Formation
In nature, aluminum oxide is found in bauxite, a mineral-rich rock. Over millions of years, weathering processes and chemical reactions cause aluminum to bind with oxygen, forming aluminum oxide. The natural cycle involves the breakdown of bauxite in the presence of water and air, where aluminum combines with oxygen to form a stable oxide layer. This natural process is crucial for the extraction of aluminum from its ore.
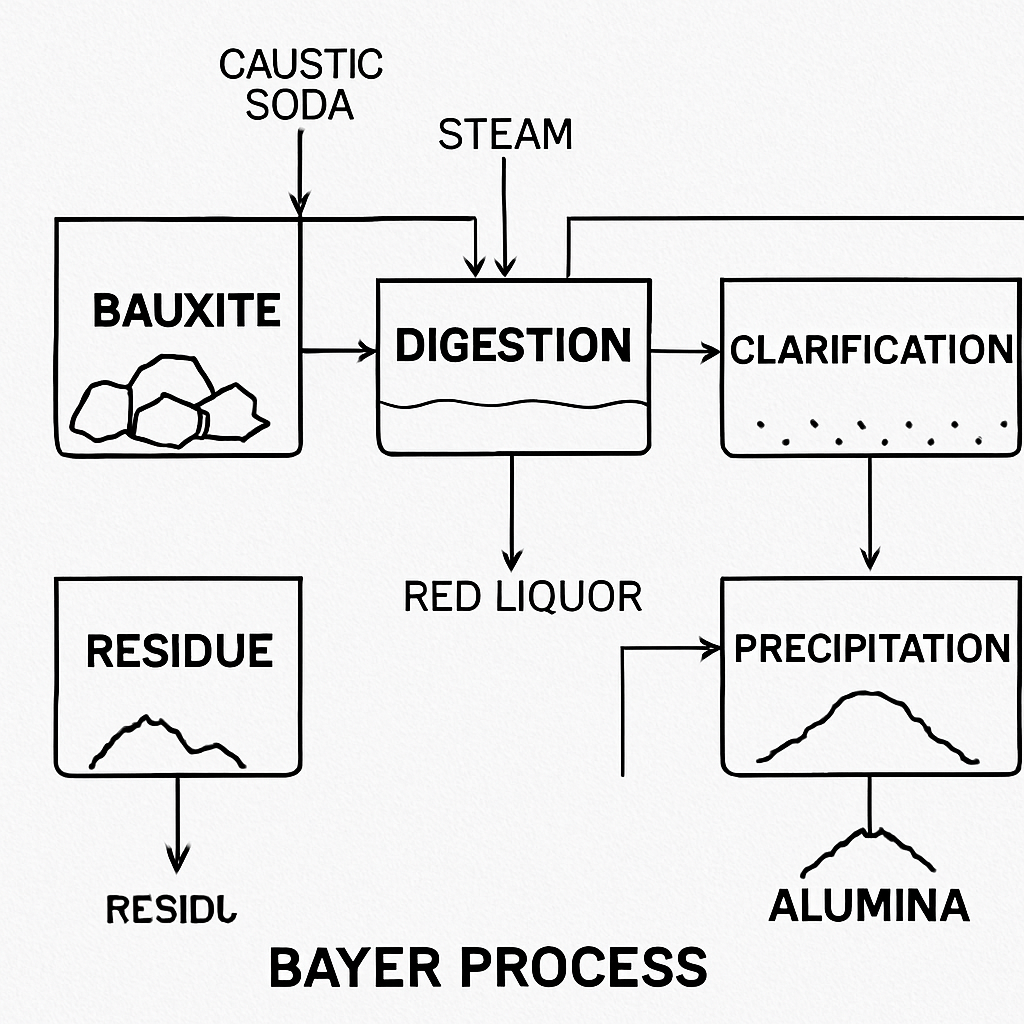
Industrial Formation
Industrially, aluminum oxide is produced from bauxite through a process called the Bayer process. This involves crushing the bauxite and treating it with sodium hydroxide, which dissolves the alumina content, leaving behind impurities. The solution is then cooled, and aluminum hydroxide precipitates out. This precipitate is heated to a high temperature, resulting in the formation of aluminum oxide. The Bayer process is efficient and widely used, providing a consistent method for producing high-purity alumina.
Alternative Production Methods
Apart from the Bayer process, other methods such as the Hall-Héroult process are employed for aluminum production, with aluminum oxide as a crucial intermediate. These methods involve electrolysis and require careful control of conditions to ensure the purity of the final product. Research continues into developing more sustainable and energy-efficient methods for aluminum oxide production.
Properties of Aluminum Oxide
Aluminum oxide is known for its hardness and high melting point, making it an excellent material for various applications.
Physical Properties
- Hardness: Aluminum oxide is incredibly hard, second only to diamond. This makes it ideal for use as an abrasive in sandpapers and cutting tools. The hardness of aluminum oxide is attributed to the strong ionic bonds between aluminum and oxygen atoms, which resist deformation.
- Melting Point: It has a high melting point of about 2072°C (3762°F), making it suitable for high-temperature applications. This property is essential for its use in refractory materials that can withstand severe thermal environments.
- Density: Aluminum oxide has a density of 3.95 to 4.1 g/cm³, which is relatively high, contributing to its durability. This density ensures that aluminum oxide is tough and able to maintain its shape under pressure.
Chemical Properties
- Inertness: Aluminum oxide is chemically inert, meaning it does not react easily with other substances. This property makes it valuable as a protective coating. Its inert nature allows it to serve as a barrier against chemical attacks, preserving the underlying material.
- Corrosion Resistance: It resists corrosion and oxidation, which is why it is used to coat aluminum surfaces, preventing them from corroding. This resistance extends the lifespan of metal products and structures, reducing maintenance costs and enhancing performance.
- Thermal Stability: Aluminum oxide remains stable at high temperatures and does not decompose, which is crucial for its use in high-temperature industrial processes. Its thermal stability ensures that it retains its properties under extreme heat.
Uses of Aluminum Oxide
The properties of aluminum oxide make it useful in a wide range of applications across different industries.
Industrial Applications
- Abrasives: Due to its hardness, aluminum oxide is used as an abrasive material in sandblasting, grinding, and polishing. These applications benefit from its durability and ability to produce smooth surfaces.
- Refractories: Its high melting point makes it suitable for lining furnaces, kilns, and reactors. Aluminum oxide refractories are essential in industries that operate at high temperatures, providing insulation and structural support.
- Ceramics: Aluminum oxide is a key ingredient in the production of advanced ceramics, used in electronic devices and high-strength materials. These ceramics are known for their electrical insulation properties and mechanical strength.
Everyday Uses
- Glass Production: It is used to make glass more durable and resistant to scratches. The addition of aluminum oxide to glass formulations enhances their clarity and toughness.
- Water Filtration: Aluminum oxide is employed in water purification systems to remove impurities. Its adsorptive properties allow it to capture contaminants, ensuring clean and safe drinking water.
- Medical Applications: In the medical field, aluminum oxide is used in prosthetics and dental implants due to its biocompatibility and strength. It provides a reliable and long-lasting material for medical devices.

by Morteza Mohammadi (https://unsplash.com/@morophoto)
Understanding the Chemical Formula
Let’s break down the chemical formula Al₂O₃ further to understand what it represents.
The Role of Aluminum
Aluminum (Al) is a metallic element that contributes to the compound’s strength and lightweight nature. In Al₂O₃, each aluminum atom shares electrons with oxygen atoms, forming strong ionic bonds. These bonds are crucial for the compound’s structural integrity, allowing it to withstand mechanical stress and environmental conditions.
The Role of Oxygen
Oxygen (O) is a non-metal that forms oxides with metals like aluminum. In Al₂O₃, oxygen atoms complete the stable structure by accepting electrons from aluminum, creating a balanced ionic compound. This interaction ensures the stability and inertness of aluminum oxide, making it resistant to chemical reactions.
Significance of the Formula
The formula Al₂O₃ is not just a representation of the compound’s composition; it is a blueprint of its chemical behavior. Understanding this formula helps in predicting how aluminum oxide will interact with other substances, its stability under different conditions, and its suitability for various applications. It also guides the production process, ensuring that the correct proportions of elements are used.
Why is the Formula Important?
Understanding the chemical formula of aluminum oxide is crucial for several reasons:
- Predicting Behavior: Knowing the formula helps predict how aluminum oxide will behave under different conditions, such as heat or chemical reactions. This knowledge is vital for designing processes and products that involve aluminum oxide.
- Manufacturing: It aids in determining the proportions needed when producing aluminum oxide for industrial purposes. Accurate formulation ensures the quality and consistency of the final product.
- Safety: Understanding the composition can help in handling and storing the compound safely, especially in industries where it is used extensively. Proper knowledge of the formula is essential for preventing accidents and ensuring safe usage.
Conclusion
Aluminum oxide is a versatile and essential compound with a simple yet powerful chemical formula, Al₂O₃. Its unique properties make it invaluable across various industries, from manufacturing to everyday applications. By understanding its composition and formation, we can appreciate the role aluminum oxide plays in modern technology and industry.
Whether you’re a student, a chemistry enthusiast, or someone working in a related field, grasping the basics of aluminum oxide and its chemical formula can provide valuable insights into its applications and importance. As industries continue to innovate and evolve, the understanding of such compounds will remain crucial for technological advancement and sustainable development.