Aluminum, renowned for its versatility and lightweight properties, is a staple across numerous industries, ranging from aerospace to construction. Its natural inclination to react with environmental elements necessitates the use of protective coatings. One such mechanism is the formation of an aluminum oxide layer, which naturally develops on the surface of aluminum. This article delves into the multifaceted benefits of the aluminum oxide layer in coatings, exploring its role in enhancing durability, providing corrosion resistance, and improving the overall performance of aluminum products.
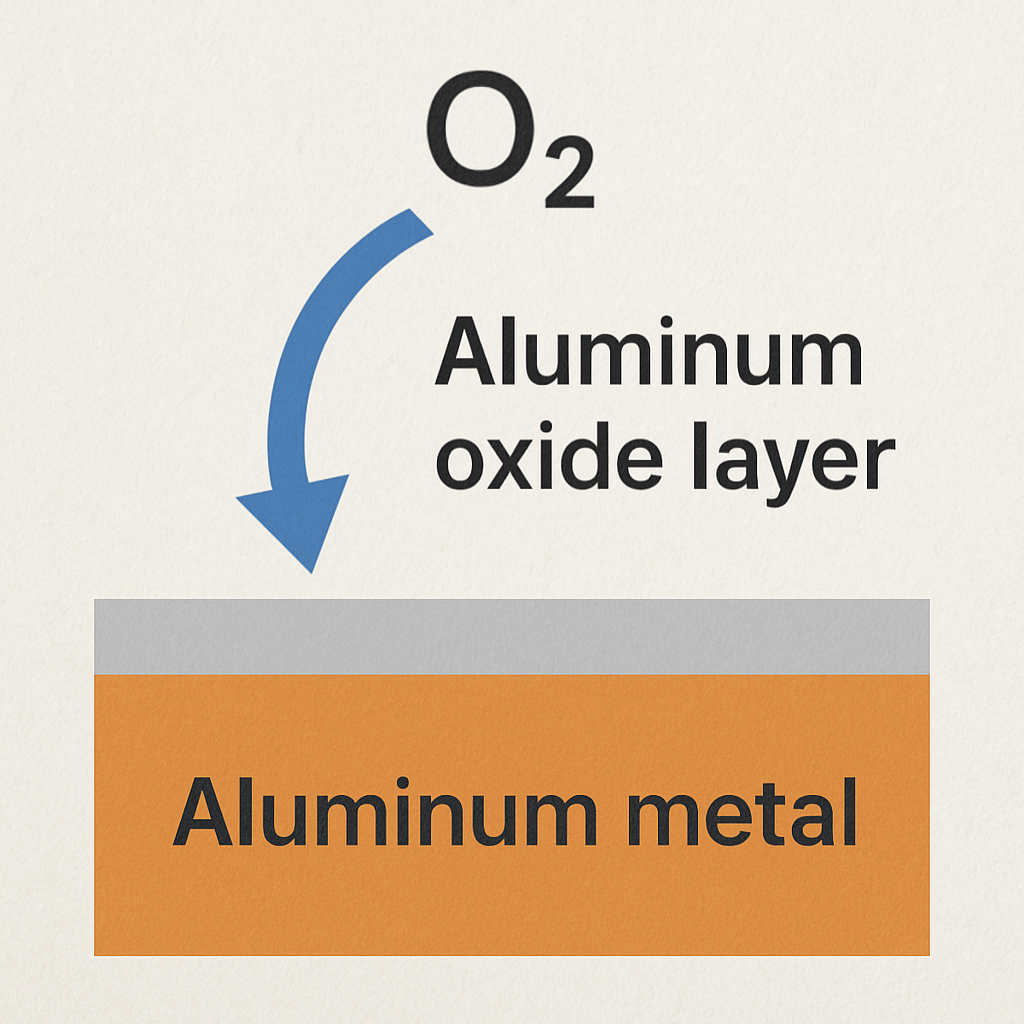
The formation of the aluminum oxide layer, also known as alumina, is an inherent process that occurs when aluminum is exposed to oxygen. This reaction results in a thin, protective layer of aluminum oxide that adheres tightly to the metal surface. The thickness of this oxide layer can vary, typically ranging from a few nanometers to several micrometers, depending on the environmental conditions and the specific surface treatment methods employed.
Key Characteristics of Aluminum Oxide Layer
- Chemical Stability: The aluminum oxide layer is chemically inert, providing a robust barrier against various corrosive agents. Its stability ensures longevity, even in harsh environments, where other coatings might degrade more quickly. The inert nature of alumina helps maintain the structural integrity of the aluminum beneath it, preventing reactions with airborne pollutants and chemicals.
- Hardness: It possesses considerable hardness, contributing to the surface’s scratch resistance. This hardness is paramount in applications where the metal surface may be subjected to mechanical wear and tear. The tough exterior not only protects the aluminum underneath but also maintains its visual appeal despite frequent contact or use.
- Transparency: The oxide layer is transparent, maintaining the aesthetic appeal of the aluminum surface. This transparency allows for the natural metallic luster of aluminum to shine through, which is particularly beneficial in consumer-facing products. It also means that any additional coatings or paints applied over the aluminum can maintain their intended color and finish without alteration.
Aluminum Surface Treatment Techniques

Surface treatments can enhance the properties of the naturally forming aluminum oxide layer. These treatments are crucial in industrial applications where enhanced performance and longevity are required.
Anodizing
Anodizing is a widely used electrochemical process that thickens the natural aluminum oxide layer. This process not only enhances corrosion resistance but also allows for the dyeing of the aluminum surface, offering aesthetic versatility.
- Process Overview: In anodizing, aluminum is immersed in an acid electrolyte bath and subjected to an electric current. This process thickens the natural oxide layer and can be precisely controlled to achieve desired thickness and color.
- Applications: Anodized aluminum finds extensive use in architectural, automotive, and consumer electronics applications. Its enhanced corrosion resistance and aesthetic flexibility make it a preferred choice for products that require both durability and visual appeal.
- Benefits: The anodized layer is integral to enhancing product lifespan, reducing maintenance needs, and providing a surface that can withstand environmental stresses without degradation.
Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation (PEO)
PEO is an advanced surface treatment technique that further enhances the properties of the aluminum oxide layer.
- Technology Insight: By applying high voltage in an electrolyte solution, PEO creates a ceramic-like oxide coating, significantly improving wear resistance and thermal stability. This method goes beyond traditional anodizing by providing a tougher, more resilient surface.
- Industry Applications: This method is particularly beneficial in aerospace and automotive industries where enhanced durability is paramount. The ceramic-like finish of PEO-treated aluminum is ideal for components exposed to extreme operational conditions.
- Advantages: PEO offers superior protection against environmental and mechanical degradation, ensuring that components maintain performance throughout their lifecycle.
Aluminum Oxide Coating: A Shield Against Corrosion
Corrosion is one of the primary concerns when it comes to metal longevity. The aluminum oxide layer acts as a formidable barrier against corrosion by preventing direct contact between the aluminum substrate and corrosive elements.
Mechanisms of Corrosion Protection
- Barrier Protection: The oxide layer acts as a physical barrier, obstructing the passage of moisture and corrosive ions. This barrier is crucial in extending the service life of aluminum components, especially in maritime and industrial environments.
- Self-Healing Properties: Minor damages to the oxide layer can be naturally repaired, as the exposed aluminum reacts with oxygen to reform the protective layer. This self-healing aspect ensures that minor abrasions do not escalate into larger problems, offering a form of passive protection.
- Electrochemical Stability: The layer reduces the electrochemical activity on the surface, diminishing the rate of corrosion. By stabilizing the electrochemical environment, the oxide layer helps maintain the metal’s integrity over time, preventing pitting and structural weakening.
Enhancing Mechanical Properties with Aluminum Oxide Layer
The aluminum oxide layer not only provides corrosion protection but also significantly enhances the mechanical properties of the aluminum surface.
Wear and Abrasion Resistance
The inherent hardness of the aluminum oxide layer contributes to its wear resistance, making it ideal for applications involving friction and mechanical stress.
- Industrial Applications: This property is particularly advantageous in the manufacturing of machine components and tools. Parts that experience constant motion or contact benefit from the reduced wear, minimizing downtime and replacement costs.
- Longevity: By reducing surface degradation, the oxide layer extends the operational lifespan of components, ensuring that machinery runs smoothly and efficiently.
- Cost Efficiency: The wear resistance leads to lower maintenance expenses and fewer replacements, resulting in cost savings over the product’s life.
Adhesion and Paint Compatibility
The oxide layer improves the adhesion of paints and coatings, ensuring long-lasting finishes and reducing the likelihood of peeling or flaking.
- Surface Preparation: Proper surface preparation ensures that paints and coatings bond effectively, resulting in a durable finish. The oxide layer’s natural texture enhances this adhesion, making it a preferred base for further treatments.
- Industry Relevance: This compatibility is crucial in industries where aesthetic and protective coatings are required. From automotive to consumer goods, the ability to maintain a pristine appearance is a significant advantage.
- Protection Enhancement: Enhanced adhesion also contributes to the protective qualities of the coating, shielding the metal from environmental damage and extending its usable life.
Aluminum Oxide Layer in Thermal Management

by Claudio Schwarz (https://unsplash.com/@purzlbaum)
Aluminum’s excellent thermal conductivity is further enhanced by the presence of an oxide layer. This property is particularly beneficial in applications requiring efficient heat dissipation, such as heat exchangers and electronic devices.
Heat Resistance
The aluminum oxide layer’s thermal stability makes it suitable for high-temperature applications, preserving the integrity of the aluminum substrate even under extreme conditions.
- High-Temperature Applications: Industries that operate under high thermal conditions, such as aerospace and automotive, benefit greatly from this property. The oxide layer ensures components retain structural strength even when exposed to heat.
- Thermal Cycling: The stability of the oxide layer helps aluminum withstand repeated thermal cycling, preventing warping or degradation that can occur with temperature fluctuations.
- Material Integrity: By maintaining material integrity at high temperatures, the oxide layer contributes to overall system reliability and safety.
Reflectivity and Insulation
The reflective nature of the oxide layer can be leveraged in thermal insulation applications, where minimizing heat absorption is essential.
- Energy Efficiency: Reflectivity is crucial in scenarios where energy efficiency is a priority, such as building materials or solar reflectors. The ability to reflect heat reduces cooling costs and enhances energy conservation.
- Insulation Properties: Beyond reflection, the oxide layer can also serve as an insulative barrier, preventing heat transfer and maintaining temperature stability within systems or structures.
- Versatility: These properties make the oxide layer a versatile tool in managing thermal environments, applicable across a wide range of industries and uses.
Factors Influencing Aluminum Oxide Layer Thickness
The thickness of the aluminum oxide layer plays a crucial role in determining its protective effectiveness. Several factors influence the growth and stability of this layer:
Environmental Conditions
Exposure to air, humidity, and pollutants can affect the rate of oxide layer formation. Controlled environments can be utilized to achieve desired oxide layer characteristics.
- Atmospheric Influence: Variations in temperature, humidity, and pollutant levels can significantly alter the rate and uniformity of oxide layer formation. Understanding these factors is key to optimizing the protective qualities of the oxide layer.
- Controlled Environments: Industrial settings can manipulate environmental conditions to consistently achieve desired oxide layer properties, enhancing product reliability and performance.
- Preventative Measures: By controlling exposure, manufacturers can minimize potential defects and ensure the oxide layer’s integrity, resulting in more consistent quality.
Surface Treatment Processes
Different surface treatment techniques can be employed to control the thickness and properties of the oxide layer, tailoring it to specific application needs.
- Customization: Techniques such as anodizing and PEO allow for precise control over oxide layer thickness, adapting the surface characteristics to meet specific industrial requirements.
- Process Selection: Selecting the appropriate surface treatment process is crucial for achieving the desired balance of protection, appearance, and functionality in the final product.
- Innovation and Adaptation: Ongoing advancements in treatment technologies provide new opportunities for optimizing aluminum surfaces, driving innovation across industries.
Alloy Composition
The presence of alloying elements can influence the formation and properties of the oxide layer, necessitating careful consideration in material selection and processing.
- Alloy Behavior: Different alloy compositions react uniquely during oxide layer formation, affecting characteristics such as thickness, hardness, and adherence. Tailoring the alloy composition is essential for optimizing these properties.
- Material Choice: Choosing the right alloy composition can enhance the oxide layer’s performance, ensuring that the final product meets specific operational and environmental challenges.
- Research and Development: Continuous research into alloy behaviors and oxide layer interactions provides insights into improving aluminum product performance and longevity.
Conclusion
The aluminum oxide layer is an integral component in enhancing the performance and longevity of aluminum products. Its ability to provide corrosion protection, improve mechanical properties, and contribute to thermal management underscores its significance in various industrial applications. By understanding the benefits and intricacies of the aluminum oxide layer, industries can harness its full potential, ensuring the durability and efficiency of aluminum-based solutions.
In conclusion, the strategic application of aluminum oxide coatings and surface treatments can significantly extend the life and functionality of aluminum products, making it a valuable investment in quality and performance. By leveraging the inherent properties of the oxide layer and utilizing advanced surface treatment techniques, manufacturers and industries can achieve superior product outcomes, meeting the demands of modern engineering and design.