Selecting the right abrasive is crucial for any project, as it determines the success or failure of the final outcome.
Abrasives are essential for surface grinding, sanding, and polishing, helping achieve the desired surface finish.
Different projects require different types of abrasives, with selection depending on the material being processed and the desired surface effect.
Industrial abrasives come in diverse forms, including grinding wheels, sanding belts, and grinding discs, each serving specific purposes.
Understanding abrasive properties is vital for ensuring optimal results and efficiency.
Safety remains a critical consideration, requiring appropriate protective measures during abrasive use.
The market offers both natural and synthetic abrasives, each type presenting distinct advantages and disadvantages.
This guide will help you navigate the world of abrasives, providing a scientific foundation for project decisions.

What Are Abrasive Materials?
Abrasive materials are substances used to wear down or smooth surfaces. They remove material through a process of rubbing or grinding.
These materials are vital in various applications. They include construction, manufacturing, and even arts and crafts.
Abrasive materials come in a wide range of hardness and textures. This variety enables them to handle different tasks effectively.
Common uses for abrasive materials include:
- Polishing surfaces to a shine
- Grinding metals or stones
- Sanding wood for a smooth finish
- Preparing surfaces for painting or coating
Typically, abrasives can be found in natural forms like garnet and emery. Meanwhile, synthetic options such as silicon carbide and aluminum oxide are widely used.
The choice of abrasive depends on the project requirements. Factors such as material type and desired finish play a role.
Understanding the function of abrasive materials can greatly impact project success. This knowledge ensures proper application and results.

Types of Abrasive Materials: Natural vs. Synthetic
Abrasive materials are classified into two main categories: natural and synthetic. Both types offer unique characteristics and applications.
Natural abrasives are mined from the earth. They include materials like garnet, emery, and diamond. Natural options are known for their intrinsic hardness and distinct textures. They are often favored for traditional and specialized tasks.
Common natural abrasives include:
- Garnet, known for medium hardness and versatility
- Emery, used in metal and woodworking
- Diamond, prized for its extreme hardness in cutting tools
On the other hand, synthetic abrasives are engineered in laboratories. They are designed for consistency and enhanced performance. Silicon carbide and aluminum oxide are the most common synthetic abrasives. These are tailored for specific industries and applications.
Popular synthetic abrasives include:
- Silicon carbide, suitable for hard materials like glass and stone
- Aluminum oxide, used broadly in sanding and metalwork
- Zirconia alumina, durable for heavy-duty grinding
Synthetic abrasives often provide more control over the properties of the material. They can be manufactured to meet diverse industry needs precisely. These materials continue to evolve with technological advances.
Choosing between natural and synthetic abrasives depends on the project’s demands and desired outcomes. Cost, durability, and availability are key considerations.

Key Properties of Industrial Abrasives
Understanding the key properties of industrial abrasives is crucial for selecting the right material. Different abrasives have distinct characteristics that affect their performance.
One important property is hardness. The hardness determines the material’s ability to cut or grind another surface. A harder abrasive can handle tougher materials, but it might wear down faster if the match is not ideal.
Essential properties of industrial abrasives include:
- Hardness: Determines material compatibility
- Toughness: Reflects resistance to fracture
- Friability: Indicates how easily the abrasive breaks under use
Another critical aspect is the grit size. Grit size affects the surface finish of the workpiece. Coarse grits remove more material quickly, while finer grits are used for finishing.
Applications often dictate the properties needed:
- High hardness for cutting tools
- Controlled friability for fine polishing
- Varied grit sizes for multi-step processes
Choosing abrasives with the appropriate properties can improve efficiency and extend tool life. Matching these properties to the project’s demands ensures optimal outcomes. Selecting well-informed properties can result in superior surface finishes and minimized material waste.

Common Types of Abrasive Materials and Their Uses
Choosing the right abrasive material involves understanding their specific applications. Various types cater to different project needs, depending on their hardness, durability, and other characteristics.
Aluminum Oxide
One of the most versatile abrasives is aluminum oxide. It’s widely used for wood, metal, and plastic due to its strength. Craftsmen prefer it for sanding and polishing because it offers a good balance between cutting speed and surface finish.
Silicon Carbide
Silicon carbide is sharper and harder, making it ideal for non-ferrous metals and stone. Its ability to cut quickly and cleanly without loading up is a key advantage. It’s perfect for glass and ceramic sanding projects.
Common Uses:
- Non-ferrous metals
- Stone and ceramics
- Glass and tiles

Zirconia Alumina
Known for its durability, zirconia alumina handles heavy-duty grinding tasks efficiently. It’s excellent for grinding metals, especially in high-pressure applications. Its longevity makes it a cost-effective choice for industrial purposes.
Ceramic Alumina
Ceramic alumina features a high fracture toughness, perfect for aggressive cutting. It performs well under high pressure, maintaining sharpness and efficiency over longer periods.
Applications:
- Metal fabrication
- Heavy stock removal
- Precision grinding

Natural and Synthetic Abrasives
Natural abrasives like garnet serve for finishing tasks, offering a fine finish on wood and soft metals. Meanwhile, synthetic abrasives provide consistency and are engineered for specific applications, enhancing performance and reliability.
Selecting the right abrasive material contributes to successful project outcomes. Each type serves distinct functions, affecting precision and speed in different ways. Understanding these differences improves both tool longevity and work quality, leading to better results.
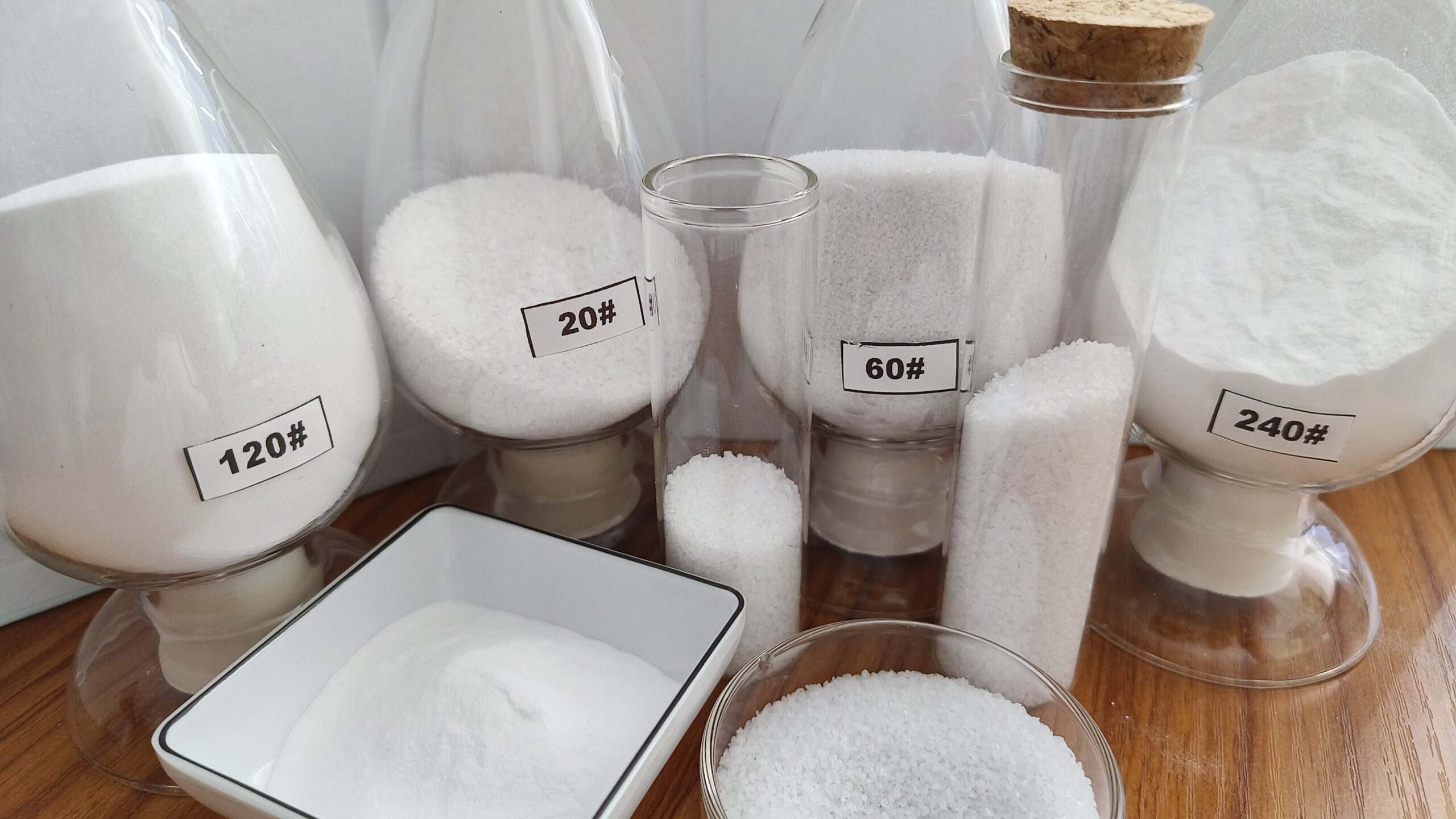
Grit Size and Its Impact on Surface Finishing
Grit size plays a crucial role in determining the finish quality of a surface. It refers to the number of abrasive particles per square inch on a sanding product. Understanding grit sizes helps in achieving the desired surface texture quickly and effectively.
Coarse grits, ranging from 40 to 60, remove material rapidly and are used for initial sanding stages. Medium grits, like those between 80 and 120, are ideal for smoothing surfaces, preparing them for finer finishes. Fine grits, from 150 to 220, deliver better smoothing and prepare surfaces for final polishing.
Grit Size Categories:
- Coarse (40-60): Rapid material removal
- Medium (80-120): Smoothing surfaces
- Fine (150-220): Preparing for final finishes
- Extra Fine (240+): Ultra-smooth polishing

Opting for the right grit size ensures efficient surface preparation and minimizes the time and effort needed to achieve a polished appearance. Each project may require different grit sequences, starting with coarse and advancing to finer grades for optimal results.
Forms of Abrasive Products: Discs, Belts, Wheels, and More
Abrasive products come in several forms, each suited for specific tasks and tools. Choosing the right form enhances the efficiency and quality of the work. Understanding these forms helps select the best abrasive product for your requirements.
Abrasive discs, for instance, are circular and come in multiple sizes. They are primarily used with angle grinders and orbital sanders. Belts, often used in belt sanders, offer continuous sanding for smoothing extensive surfaces. Abrasive wheels, typically attached to bench grinders, are ideal for sharpening tools and metalwork.
Common Forms of Abrasive Products:
- Discs: Suitable for grinders and sanders
- Belts: Used for smoothing large areas
- Wheels: For sharpening and metal finishing

Understanding the function of each form ensures better project results. Choose based on the task, tool compatibility, and material involved. Using the correct form can reduce labor, minimize material waste, and enhance finish quality.
How to Choose the Right Abrasive Material for Your Project
Selecting the right abrasive material is crucial for achieving desired outcomes. It can vastly improve efficiency and finish quality. Understand your project’s requirements to make an informed choice.
First, consider the material you are working on. Metal, wood, and plastic all interact differently with abrasives. For instance, aluminum oxide is versatile, while silicon carbide works better on stone and glass.
Next, determine the project’s scope and finish. Coarse abrasives remove material quickly but leave rough surfaces. Finer grits provide a smoother finish. Match the grit size to your project’s needs for optimal results.
Questions to Consider:
- What material am I working with?
- What finish am I aiming to achieve?
Don’t forget to think about the tools available to you. Machines like angle grinders and handheld sanders require different abrasives. Ensure that the abrasives you select are compatible with your tools to avoid inefficiency or damage.
Finally, assess environmental conditions and safety needs. Opt for wet abrasives to reduce dust if needed, and always prioritize safety gear during use. This approach leads to a safer work environment and better results.
Key Factors in Selection:
- Material type
- Desired finish
- Tool compatibility
- Safety considerations
By analyzing these factors, you ensure the correct abrasive is chosen. This will enhance performance, reduce project time, and achieve your desired quality.
Safety Tips When Working with Abrasive Materials
Safety is paramount when using abrasive materials. Improper handling can lead to injuries or damage. Follow these tips to ensure safe practices.
Always wear appropriate protective gear, including gloves, goggles, and a dust mask. This equipment shields you from harmful debris and dust particles that can be hazardous to your health.
Maintain a clean and organized workspace. Clutter increases the risk of accidents. Ensure all tools are in good condition to prevent malfunctions.
Essential Safety Gear:
- Safety goggles
- Dust mask or respirator
- Protective gloves

Be mindful of proper ventilation in your workspace. Adequate airflow reduces dust and fume inhalation. Additionally, inspect abrasive tools for wear or damage before use. This reduces the likelihood of accidents and extends tool life.
Innovations and Trends in Abrasive Materials
The field of abrasive materials is ever-evolving. Innovations focus on enhancing efficiency and sustainability. Manufacturers are exploring new synthetic abrasives that offer improved consistency and performance.
Recent trends include the development of eco-friendly abrasives. These materials aim to minimize environmental impact while maintaining effectiveness. Another trend is the integration of advanced coatings on abrasive products for better durability and heat resistance.
Notable Trends:
- Eco-friendly materials
- Improved synthetic abrasives
- Advanced coatings

As technology advances, abrasive materials continue to improve. This evolution provides enhanced outcomes for a variety of projects across industries. Keeping abreast of trends can aid in selecting superior abrasives for your needs.
Environmental and Cost Considerations
When selecting abrasive materials, environmental impact is a key consideration. Dust control and waste management can affect the sustainability of a project. Recycling abrasives, when possible, helps reduce waste and support eco-friendly practices.
Cost is another important factor to consider. Prices vary significantly depending on the type and quality of the abrasive materials. More durable abrasives might require a higher initial investment, but they often last longer and offer better performance.
Considerations:
- Dust control
- Waste management
- Recycling potential
- Cost vs. durability balance
Balancing cost with environmental concerns can lead to more sustainable and economical project outcomes.
Maintenance, Storage, and Longevity of Abrasive Materials
Proper maintenance extends the lifespan of abrasive materials. Regular inspections help detect wear and tear early. This ensures you replace them before they become ineffective.
Storage conditions are crucial for longevity. Keep abrasive materials dry and away from extreme temperatures. This prevents deterioration and maintains their effectiveness.
Key Tips:
- Inspect for wear regularly
- Store in a dry, stable environment
- Avoid exposure to extreme temperatures
Following these practices helps ensure that your abrasives remain efficient and ready for use when needed.
Conclusion: Achieving the Best Results with the Right Abrasive Material
Selecting the right abrasive material is crucial for successful project outcomes. Consider the material, grit size, and intended finish to make an informed choice. These factors greatly influence the efficiency and quality of your work.
Understanding different abrasive types helps match the tool to the task. This knowledge not only saves time but also enhances surface quality. Always prioritize the compatibility between abrasive materials and your specific needs.
Remember, using the correct abrasive material leads to better adhesion and precise results. With proper selection and use, you can achieve smooth finishes and well-prepared surfaces. Embrace the power of abrasives to elevate your projects, ensuring they meet desired standards.