Alumina, chemically known as aluminum oxide (Al2O3), is a white crystalline substance used primarily in the production of aluminum. The transformation of bauxite ore into alumina is a multi-stage process involving extraction, refining, and purification.
Bauxite, the primary raw material for alumina, is an ore rich in aluminum oxide minerals. It is mined through diverse techniques, tailored to its geographical locati0n and composition. Open-pit mining is often employed in regions where the ore is close to the surface, while underground mining is used for deeper deposits. Beyond alumina production, bauxite is integral in creating abrasives, cement, and chemicals. Understanding the multifaceted uses of bauxite underscores its pivotal role in a variety of industrial processes and products.
The Alumina Manufacturing Process
The production of alumina from bauxite involves the Bayer process, a well-established method that includes crushing the ore and treating it with sodium hydroxide to dissolve the aluminum oxide. This method begins with the crushing of bauxite, followed by its dissolution in a hot sodium hydroxide solution, which separates aluminum oxide from impurities. The resulting solution is then cooled, allowing the aluminum hydroxide to precipitate out. Subsequent filtration and calcination at high temperatures result in the production of anhydrous alumina, a critical step that transforms the material into a form suitable for aluminum smelting.
Environmental Considerations in Alumina Production
The production process, while efficient, raises significant environmental concerns. The Bayer process generates a byproduct known as red mud, a highly alkaline residue that poses disposal challenges. Companies are investing in research to develop more sustainable disposal methods and explore ways to repurpose red mud into useful materials. Furthermore, the energy-intensive nature of the production process necessitates a focus on renewable energy sources and energy-saving technologies to reduce the carbon footprint of alumina manufacturing.
Global Landscape of Alumina Production
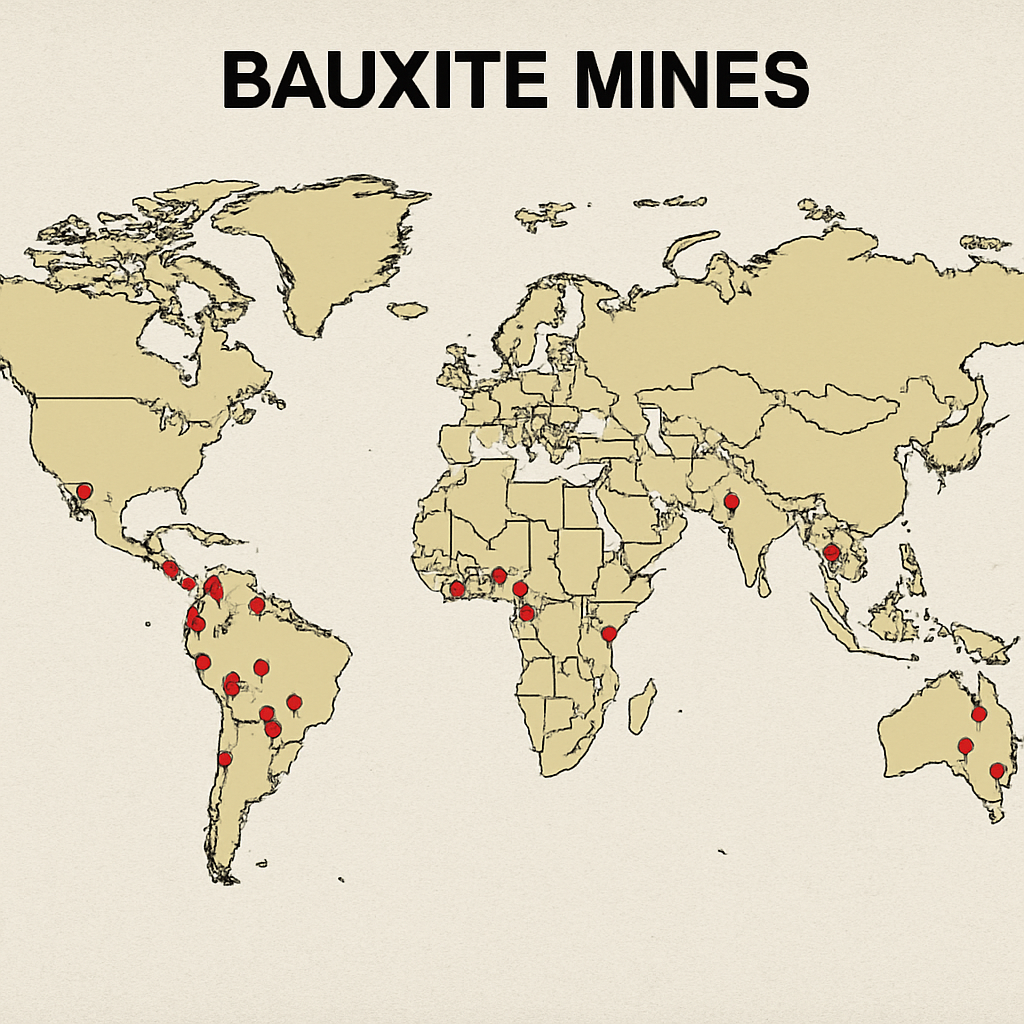
The distribution of bauxite mines and alumina refineries across the globe is influenced by geological, environmental, and economic factors. Key regions for bauxite mining include Australia, Guinea, China, and Brazil. These countries not only have substantial bauxite reserves but also possess the infrastructure necessary for large-scale alumina production.
Major Bauxite Mines and Alumina Refineries
Bauxite mining and alumina refining are concentrated in areas where geological conditions favor the presence of high-quality ore. Australia, Guinea, China, and Brazil are home to some of the largest bauxite mines globally, supported by sophisticated infrastructure that enables efficient extraction and processing. These regions have developed extensive supply chains and logistical networks to facilitate the transportation of bauxite to refineries and export markets.
Australia: A Leading Alumina Producer
Australia stands out as a top producer of bauxite and alumina, with significant mining operations in Western Australia and Queensland. The country’s mining sector benefits from advanced technology and sustainable practices, making it a leader in alumina manufacturing. Australian companies focus on minimizing environmental impact through innovative waste management strategies and energy-efficient operations. The country’s commitment to research and development ensures the continuous improvement of alumina production techniques.
Guinea: Rich Reserves and Rising Production
Guinea, in West Africa, boasts some of the world’s richest bauxite deposits. The country’s strategic locati0n and investment in mining infrastructure have led to increased alumina production, positioning it as a formidable player in the global market. Guinea’s government has implemented policies to attract foreign investment and enhance local expertise, further boosting its mining sector. The development of new refineries and expansion of existing ones are integral to Guinea’s strategy for capitalizing on its vast mineral wealth.
China: Balancing Demand and Domestic Production
China, a major consumer of alumina, has invested heavily in domestic production to meet its industrial needs. Despite having substantial bauxite reserves, China’s rapid industrialization necessitates imports to supplement its alumina supply. The country’s focus on self-sufficiency drives investment in mining technology and refinery capacity, while strategic partnerships with bauxite-rich countries secure a steady import flow. China’s balancing act between domestic production and imports highlights its complex role in the global alumina market.
Brazil: A Growing Alumina Powerhouse
Brazil’s bauxite reserves and recent investments in refinery capacity have bolstered its position in the global alumina market. The country’s commitment to expanding its mining operations ensures a steady increase in alumina output. Brazil’s government and private sector collaborate on initiatives to enhance mining efficiency and environmental management. These efforts, combined with Brazil’s strategic locati0n and transport infrastructure, solidify its role as a key player in the alumina industry.
North American Contributions: Bauxite Mines in the U.S.
While the United States does not lead in bauxite production, it plays a significant role in the alumina supply chain through refining and recycling. The bauxite mines in the U.S., though limited, contribute to domestic alumina production, ensuring a degree of self-sufficiency. American refineries focus on innovative recycling techniques to recover aluminum from scrap, reducing reliance on primary alumina. This approach not only supports sustainability but also strengthens the U.S. position in the global aluminum market.
The Chemistry Behind Alumina: From Molecule to Metal
Understanding the chemistry of alumina is crucial for appreciating its transformation into aluminum. The alumina molecule, Al2O3, undergoes electrolysis in the Hall-Héroult process to produce aluminum metal. This chemical journey from alumina compound to refined aluminum underscores the complexity and ingenuity of metallurgical processes.
Is Alumina an Element?
While alumina is not an element, it is a compound composed of aluminum and oxygen. Its unique properties make it indispensable in producing aluminum and other industrial applications, including ceramics, refractories, and electronics. Alumina’s high melting point, hardness, and thermal stability render it ideal for use in demanding environments, such as high-temperature furnaces and electronic components. The versatility of alumina extends beyond metal production, contributing to innovations in various high-tech industries.
Electrolysis and the Hall-Héroult Process
The Hall-Héroult process, a cornerstone of aluminum production, involves the electrolysis of alumina dissolved in molten cryolite. This process separates aluminum from oxygen, resulting in pure aluminum metal. The energy-intensive nature of the process drives ongoing research into enhancing efficiency and reducing environmental impact. Innovations such as inert anodes and alternative electrolytes are explored to lower carbon emissions and improve sustainability in aluminum manufacturing.
Alumina’s Role in Advanced Materials
Alumina’s properties extend its application beyond traditional uses, playing a crucial role in advanced materials. Its wear resistance and insulating characteristics make it essential in creating cutting-edge ceramics and composites. Researchers are exploring new ways to incorporate alumina into nanomaterials, offering potential breakthroughs in electronics, aerospace, and biomedical fields. The continuous evolution of alumina applications highlights its significance in driving technological advancements.
Economic and Environmental Implications
The alumina industry, like many extractive industries, faces economic and environmental challenges. These include fluctuating commodity prices, geopolitical tensions, and environmental concerns related to bauxite mining and alumina refining.
Sustainable Alumina Mining and Production
Efforts to minimize the environmental impact of alumina production focus on reducing energy consumption, managing tailings, and rehabilitating mining sites. Advancements in technology and sustainable practices are pivotal in addressing the ecological footprint of the alumina industry. Companies invest in renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, to power operations and reduce reliance on fossil fuels. Rehabilitation projects aim to restore biodiversity and ecosystem health in mined areas, ensuring long-term environmental sustainability.
Economic Significance of Alumina
The production and export of alumina contribute significantly to the economies of producing countries. The alumina market’s dynamics, influenced by global demand for aluminum, underscore the importance of strategic planning and investment in mining infrastructure. Countries with rich bauxite reserves leverage their resources to attract foreign investment and drive economic growth. The alumina industry supports job creation and technological development, enhancing the economic resilience of producing nations.
Geopolitical Factors and Market Dynamics
Geopolitical factors play a crucial role in shaping the alumina market, with trade policies and international relations impacting supply chains. Tariffs, trade agreements, and regional conflicts can influence the availability and price of alumina, affecting global industry dynamics. Companies and governments must navigate these challenges through strategic alliances and diversification of supply sources. Understanding the geopolitical landscape is essential for stakeholders to make informed decisions and mitigate risks in the alumina sector.
Conclusion: The Future of Alumina Mining and Production
As global demand for aluminum continues to rise, the importance of alumina as a critical input cannot be overstated. The exploration of global sources of alumina reveals a complex network of geological, economic, and environmental factors that shape the industry. The ongoing pursuit of innovation and sustainability will determine the future landscape of alumina mining and production, ensuring that it meets the needs of a rapidly evolving world.

by Stupidmen City (https://unsplash.com/@faishalzaky)
Innovation and Technological Advancements
The future of alumina mining and production hinges on innovation and technological advancements. Breakthroughs in extraction and refining processes aim to enhance efficiency and reduce environmental impact. The integration of digital technologies, such as AI and IoT, optimizes mining operations and improves resource management. Continuous investment in research and development is crucial for driving progress and maintaining competitiveness in the global market.
Collaborative Efforts for Sustainability
Sustainability in the alumina industry requires collaboration among stakeholders, including governments, companies, and communities. Joint initiatives focus on developing sustainable practices, sharing knowledge, and implementing best practices across the industry. Community engagement and transparent communication are vital for fostering trust and ensuring that mining activities benefit local populations. Collaborative efforts pave the way for a more sustainable and equitable future for alumina production.
Strategic Planning for a Dynamic Future
Strategic planning is essential for navigating the dynamic future of the alumina industry. Companies and governments must anticipate market trends, adapt to changing regulations, and invest in resilient infrastructure. Diversifying supply sources and exploring new markets are key strategies for mitigating risks and capitalizing on opportunities. By understanding the intricacies of the alumina supply chain, stakeholders can make informed decisions that drive growth and sustainability in this vital industry.